|
op·er·a·tion (op |
|
1. any act performed with instruments or by the hands of a
surgeon; a surgical procedure. 2. the process or act of
functioning, doing, or performing. |
|
|
|
Operation |
|
|
|
|
|
For terms not found here, see also method, procedure, repair,
surgery, technique, or the specific type of operation such as
amputation. |
|
|
|
Abbe operation, attachment of a triangular,
full-thickness flap from the median portion of the lower lip to
fill a defect in the upper lip. |
|
Adams operation, subcutaneous
intracapsular division of the neck of the femur for ankylosis of
the hip.subcutaneous division of the palmar fascia at various
points for Dupuytren contracture.excision of a wedge-shaped
piece from the eyelid for relief of ectropion. |
|
Akin operation, resection of the medial
prominence of the first metatarsal head and cuneiform osteotomy
of the proximal phalanx of the great toe, done for hallux valgus. |
|
Albee operation, operation for ankylosis of
the hip, consisting of cutting off the upper surface of the head
of the femur and freshening a corresponding point on the
acetabulum, and permitting the two freshened surfaces to rest in
contact. |
|
Albee-Delbet operation, an operation for
fracture of the neck of the femur, done by drilling a hole
through the trochanter and the neck and head of the femur and
inserting a bone peg in this hole. |
|
Albert operation, excision of the knee to
secure ankylosis for the cure of flail joint. |
|
Alexander operation, Alexander-Adams operation,
shortening of the round ligaments to repair
displacement of the uterus. |
|
Alouette operation, see under
amputation. |
|
Ammon operation, blepharoplasty
by a flap from the cheek.dacryocystotomy.for epicanthus:
resection of a spindle-shaped piece of skin over the bridge of
the nose, undermining the flaps of the epicanthal fold, and
closing with sutures. |
|
Anagnostakis operation, an operation for
entropion.an operation for trichiasis. |
|
Aries-Pitanguy operation, see
under mammaplasty. |
|
Baldy operation, Baldy-Webster
operation, Webster o. |
|
Barkan operation, goniotomy. |
|
Barker operation, an excision of the hip
joint by an anterior cut.a special method of excising the
astragalus by an incision extending from just above the external
malleolus forward and inward to the dorsum of the foot. |
|
Barraquer operation, phacoerysis. |
|
Barsky operation, an operation for repair of
a cleft hand with a missing central ray and a deep central
V-shaped cleft, consisting of closing the cleft, bringing the
ring and index fingers closer together, and correcting the
associated syndactyly, if present. |
|
Barton operation, an operation for ankylosis
consisting of sawing through the bone and removing a V-shaped
piece. |
|
Basset operation, a method of dissecting the
inguinal glands in radical operations for cancer of the vulva. |
|
Bassini operation, repair of
inguinal hernia, with high ligation of the sac, reinforcement of
the floor of the canal, and placement of the spermatic cord
under the external oblique anastomosis. |
|
Beer operation, a flap method for cataract. |
|
Belsey Mark IV operation, fundoplication for
gastroesophageal reflux with the fundus being wrapped 270
degrees around the circumference of the esophagus, leaving its
posterior wall free; done through a thoracic incision. Called
also Belsey Mark IV fundoplication. |
|
Berger operation,
interscapulothoracic amputation. |
|
Berke operation, a modification of the
Blaskovics operation for ptosis of the upper eyelid, with
resection of the levator muscle through a skin incision and
excision of excess muscle.a modification of the Motais operation
for ptosis of the upper eyelid, with suspension of the ptotic
lid from the superior rectus muscle. |
|
Bier operation, see under
amputation. |
|
Biesenberger operation, see under
mammaplasty. |
|
Billroth operation, either of two operations
with partial resection of the stomach and anastomosis of the
remaining stomach to either the duodenum (Billroth I) or the
jejunum (Billroth II). Called also Billroth gastrectomy or
gastroenterostomy. |

|
|
Blair-Brown operation, repair of a cleft lip
by the use of a lateral flap one-half the length of the lip. |
|
Blalock-Hanlon operation, a palliative
operation for transposition of the great vessels, consisting of
the creation of an interatrial septal defect. |
|
Blalock-Taussig operation, the side-to-side
anastomosis of the left subclavian artery to the left pulmonary
artery (sometimes the right subclavian to the right pulmonary
artery) in order to shunt some of the systemic circulation into
the pulmonary circulation; performed as palliative treatment of
tetralogy of Fallot or other congenital anomalies associated
with insufficient pulmonary arterial flow. |
|
Blaskovics operation, an operation for
ptosis of the upper eyelid, consisting of excision of the
levator muscle and the tarsus through a conjunctival approach. |
|
Bricker operation, see under
technique. |
|
Brock operation, transventricular
closed valvotomy. |
|
Browne operation, a type of urethroplasty
for repair of hypospadias; an intact strip of epithelium is left
on the ventral surface of the penis to form the roof of the
urethra, and the floor of the urethra is formed by
epithelialization from the lateral wound margins. Called also
Denis Browne o. |
|
Brunschwig operation, pelvic
exenteration. |
|
Buck operation, cuneiform excision of the
patella and the ends of tibia and fibula. |
|
Burow operation, a method of excising
triangles of skin at the base of the pedicle of a skin flap to
facilitate advancement. |
|
Caldwell-Luc operation,
antrostomy in which an opening is made into the maxillary sinus
by way of an incision into the supradental fossa opposite the
premolar teeth, usually done to remove tooth roots or abnormal
tissue from the sinus.in compound zygomaticomaxillary fractures,
the packing of the maxillary sinus by approaching the antrum
through the canine fossa of the maxilla above the tooth apices,
thus allowing reduction of displaced fragments of the zygoma by
upward and outward pressure. Called also Luc o. |
|
Carpue operation, Indian
rhinoplasty. |
|
Cecil operation, a two-stage urethroplasty
for hypospadias repair, with construction of a new urethral
segment buried in the scrotum, and later by separation of the
new urethra from the scrotum. Called also Cecil urethroplasty. |
|
Charles operation, treatment of
elephantiasis and other types of massive lymphedema of the lower
limb by excision of subcutaneous tissue followed by skin
grafting. |
|
Chopart operation, see under
amputation. |
|
Colonna operation, a reconstruction
operation for intracapsular fracture of the femoral neck.a
common type of capsular arthroplasty of the hip. |
|
Commando operation, an operation for
management of oral cancer, consisting in resection of the
primary lesion and the regional lymphatic nodes. |
|
concrete operations, a stage in reasoning or
functioning usually seen in children between the ages of
approximately 7 and 11, following the stage of preoperational
thinking and preceding that of formal operations; it is
characterized by comprehension of relational terms, decrease in
egocentricity and increase in the ability to appreciate the
perspective of others, understanding of the reversibility of
events and ideas as well as of conservation of volume and
quantity, and the beginning of logical thought, although it is
initially restricted to objects immediately present. |
|
Conway operation, see under
mammaplasty. |
|
Cooper ligament operation, McVay
repair. |
|
cosmetic operation, one intended to remove
or correct a deformity in an esthetically acceptable manner. |
|
Cotte operation, removal of the presacral
nerve. |
|
Dandy operation, trigeminal rhizotomy using
an approach through the posterior cranial fossa. |
|
Daviel operation, extraction of cataract
through a corneal incision without cutting the iris. |
|
Denis Browne operation, Browne o. |
|
Denonvilliers operation, plastic correction
of a defective ala nasi by transferring a triangular flap from
the adjacent side of the nose. |
|
Dieffenbach operation, plastic closure of
triangular defects by displacing a quadrangular flap toward one
side of the triangle. |
|
Dittel operation, an early
treatment for hypertrophy of the prostate, consisting of
enucleation through an external incision. |
|
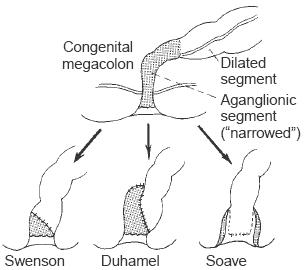
Duhamel operation, the treatment of
congenital megacolon by a modification of the pull-through
operation and establishment of a longitudinal anastomosis
between the proximal ganglionated segment of colon and the
rectum, leaving the rectum in situ. See illustration at Swenson
o. |
|
Dührssen operation, vaginofixation of the
uterus. |
|
Dupuy-Dutemps operation, blepharoplasty of
the lower lid with tissue from the opposing lid. |
|
Dupuytren operation, shoulder
disarticulation. |
|
Elliot operation, a method of trephining the
sclerocornea for the relief of increased tension in glaucoma. |
|
Emmet operation, a method of
repairing a lacerated perineum.trachelorrhaphy.surgical creation
of a vesicovaginal fistula to secure drainage of the bladder in
cystitis. |
|
equilibrating operation, tenotomy of the
direct antagonist of a paralyzed eye muscle. |
|
Esser operation, epithelial
inlay. |
|
Estes operation, implantation of an ovary
into a uterine cornu; performed to establish fertility when the
uterine tubes are absent. |
|
Estlander operation, resection of one or
more ribs in empyema so as to allow the chest wall to collapse
and close the abnormal cavity; of historical interest.rotation
of a triangular flap from the side of the lower lip to fill a
defect in the lateral upper lip. |
|
Eversbusch operation, an operation for
ptosis of the upper eyelid, consisting of resection of the
levator muscle through a skin incision. |
|
exploratory operation, surgical incision
into an area of the body followed by inspection and palpation of
organs and tissues to determine the cause of unexplained
symptoms. |
|
Fergusson operation, removal of
the maxilla through an incision running along the junction of
the nose with the cheek, around the ala of the nose to the
median line, and then down to bisect the upper lip. Called also
Fergusson incision. |
|
Finney operation, see under
pyloroplasty. |
|
flap operation, any operation
involving the raising of a flap of tissue.in periodontics, an
operation to secure greater access to granulation tissue and
osseous defects, consisting of detachment of the gingivae, the
alveolar mucosa, and/or a portion of the palatal mucosa.see
under amputation. |
|
formal operations, a form of thinking
following the stage of concrete operations and representing the
final, most mature state of thinking; usually occurring after
the age of 11 and characterized by the emergence of true logical
thought, with the capability for deductive reasoning, abstract
thinking, formulation and testing of hypotheses, appreciation
for multiple perspectives on an issue, and the manipulation of
ideas and concepts. |
|
Fothergill operation, Manchester
o. |
|
Frazier-Spiller operation,
trigeminal rhizotomy using an approach through the middle
cranial fossa. |
|
Fredet-Ramstedt operation,
pyloromyotomy. |
|
Freyer operation, a method formerly used for
prostatic hypertrophy, using suprapubic enucleation. |
|
Fukala operation, removal of the lens of the
eye for the treatment of marked myopia. |
|
Fuller operation, a former method
of treating an abscessed seminal vesicle by draining it through
a perineal incision. |
|
Gifford operation, delimiting
keratotomy. |
|
Gilliam operation, an operation for
retroversion of the uterus by drawing a loop of each round
ligament through the abdominal wall and fixing the loops to the
abdominal fascia. |
|
Gillies operation, operation for correction
of ectropion utilizing a split-thickness skin graft and a mold.a
technique for reducing fractures of the zygoma and zygomatic
arch through an incision in the temporal region above the
hairline. |
|
Girdlestone operation, see under
resection. |
|
Glenn operation, an operation for congenital
cyanotic heart disease, consisting of anastomosis of the
superior vena cava to the right pulmonary artery. |
|
Gonin operation, treatment of retinal
detachment by thermocautery of the fissure in the retina
performed through an opening in the sclera. |
|
Graefe operation, removal of the cataractous
lens by a scleral cut, with laceration of the capsule and
iridectomy. |
|
Gritti operation, see under
amputation. |
|
Guyon operation, see under
amputation. |
|
Halsted operation, radical
mastectomy. |
|
Hancock operation, see under
amputation. |
|
Hartley-Krause operation, excision of the
gasserian ganglion and its roots to relieve trigeminal
neuralgia; of historical interest. |
|
Hartmann operation, see under
procedure. |
|
Haultain operation, a
modification of the Huntington operation for replacement of a
chronically inverted uterus, involving a posterior incision in
the uterus through the cervical ring. |
|
Heine operation, cyclodialysis in glaucoma. |
|
Heineke-Mikulicz operation, see
under pyloroplasty. |
|
Heller operation,
esophagocardiomyotomy. |
|
Herbert operation, displacement of a
wedge-shaped flap of sclera in order to form a filtering
cicatrix in glaucoma. |
|
Hey operation, see under
amputation. |
|
Hibbs operation, a spinal fusion operation
done by fracturing the spinous processes of the vertebrae and
pressing the tip of each downward to rest in the denuded area
caused by the fracture of its elbow below. |
|
Hoffa operation, Hoffa-Lorenz
operation, Lorenz o. |
|
Holth operation, excision of the sclera by
punch operation. |
|
Homans operation, a formerly
common treatment for elephantiasis and other types of massive
edema of the lower limb, consisting of excision of subcutaneous
tissue and redundant skin on the lateral and medial aspects. |
|
Horsley operation, excision of an area of
motor cortex for relief of athetoid and convulsive movements of
an upper extremity; of historical interest. |
|
Huggins operation, orchiectomy done to treat
cancer of the prostate. |
|
Hunter operation, a former method of
treating aneurysm, consisting of ligation of the artery on the
proximal side of the aneurysm above the first collateral. |
|
Huntington operation, transabdominal repair
of a chronically inverted uterus. It is done by grasping the
invaginated portion of the uterus with forceps; as the uterus is
pulled up, additional forceps are placed sequentially lower
down, and upward traction is applied. After the uterus is in
place, the position is maintained by packing through the vagina. |
|
Indian operation, see under
rhinoplasty. |
|
interposition operation, Watkins
o. |
|
interval operation, an operation performed
during the interval between two acute attacks of a disease, as
in appendicitis. |
|
Irving operation, see under
technique. |
|
Italian operation, tagliacotian
rhinoplasty. |
|
Jaboulay operation,
hemipelvectomy. |
|
Jantene operation, a type of
arterial switch procedure (q.v.). |
|
Kasai operation,
portoenterostomy. |
|
Kazanjian operation, a technique of surgical
extension of the buccal vestibular sulcus of edentulous ridges
to increase their height and to improve denture retention.the
use of extraskeletal fixation for support in compound
zygomaticomaxillary fractures: a small hole is drilled through
the infraorbital rim, and a stainless steel wire is inserted
with both ends brought out through the wound, where they are
twisted together into a loop or hook. Rubber band traction
between the suspension wire and an outrigger on a head cap
provides support for the zygomatic fragments. |
|
Keller operation, sagittal resection of the
medial prominence of the first metatarsal head and excision of
the base of the proximal phalanx of the great toe; done for
hallux valgus. |
|
Kelly operation, see under
plication. |
|
Killian operation, excision of the anterior
wall of the frontal sinus, removal of the diseased tissue, and
formation of a permanent communication with the nose. |
|
Killian-Freer operation, submucous resection
of the nasal septum, including the septal cartilage, vomer, and
perpendicular plate of the ethmoid. |
|
King operation, arytenoidopexy. |
|
Knapp operation, treatment of
cataract by the formation of a peripheral opening in the capsule
behind the iris, without iridectomy. |
|
Kondoleon operation, a formerly common
treatment for elephantiasis and other types of lymphedema by the
removal of strips of subcutaneous tissue; it was later modified
to the Homans operation. |
|
Körte-Ballance operation, anastomosis of the
facial and hypoglossal nerves. |
|
Kraske operation, removal of the coccyx and
part of the sacrum for access to rectal carcinoma. |
|
Krause operation, extradural
excision of the gasserian ganglion for trigeminal neuralgia; of
historical interest. |
|
Krönlein operation, resection of the outer
wall of the orbit for the removal of an orbital tumor without
excising the eye. |
|
Küstner operation, replacement of an
inverted uterus through an incision made in the cervix and
uterus along the posterior surface. |
|
Lagrange operation,
sclerectoiridectomy. |
|
Landolt operation, the formation of a lower
eyelid with a double pedicle or bridge flap of eyelid skin taken
from the upper lid. |
|
Lapidus operation, a procedure for
correction of hallux valgus, involving wedge resection and
fusion of the innermost cuneometatarsal joint and establishment
of a bridge between the bases of the first and second
metatarsals. |
|
Larrey operation, see under
amputation. |
|
Latzko operation, Latzko cesarean
section.a method of repairing a vesicovaginal fistula by using
mucosa denuded from the posterior wall of the vagina as a flap
to cover the fistula. |
|
Le Fort operation, Le Fort-Neugebauer operation,
the operation of uniting the anterior and
posterior vaginal walls along the middle line for the repair or
prevention of prolapse of the uterus. |
|
Lempert fenestration operation, an operation
for otosclerosis, consisting of drilling a small window into the
lateral semicircular canal and then placing a flap of skin over
the fistula. |
|
Lisfranc operation, see under
amputation.shoulder disarticulation. |
|
Lorenz operation, an operation
for developmental dysplasia of the hip, consisting of reduction
of the dislocation, and keeping the head of the femur fixed
against the rudimentary acetabulum until a socket is formed. |
|
Lowsley operation, an operation
for repair of simple epispadias, consisting of closing the cleft
urethra, splitting the glans, and burying the repaired urethra
deep in the soft tissue so that its orifice will be at the
normal site. |
|
Luc operation, Caldwell-Luc o. |
|
Lynch operation, incision of the frontal
sinus and removal of its floor and contents; done in cases of
expanding mucoceles, pyoceles, and tumors of the sinus. |
|
McBride operation, resection of the medial
prominence of the first metatarsal head, medial capsulorrhaphy,
resection of the fibular sesamoid, and transfer of the adductor
tendon to the neck of the first metatarsal; done for hallux
valgus. |
|
McDonald operation, an operation for
incompetent cervix, in which the cervical os is closed with a
purse-string suture. |
|
McGill operation, suprapubic
transvesical prostatectomy. |
|
McVay operation, see under
repair. |
|
magnet operation, removal of a fragment of
steel or iron from the eyeball by means of a powerful magnet. |
|
major operation, an operation of
major surgery (q.v.). |
|
Manchester operation, an operation for
uterine prolapse comprising dilation and curettage, anterior
repair, amputation of the vaginal portion of the cervix,
shortening of the cardinal ligaments, and posterior
colpoperineorrhaphy. |
|
Marshall-Marchetti-Krantz
operation, an operation for the correction of stress
incontinence; the anterior portion of the urethra, vesical neck,
and bladder are sutured to the posterior surface of the pubic
bone. |
|
Matas operation,
endoaneurysmorrhaphy. |
|
Maydl operation, one of the pioneering
treatments for exstrophy of the bladder, attaching the ureters
to the rectum (see ureterorectostomy). |
|
Meller operation, an operation for excision
of the tear sac. |
|
Mikulicz operation, Heineke-Mikulicz
pyloroplasty.Vladimiroff-Mikulicz amputation. |
|
Miles operation, surgical treatment for
cancer of the lower sigmoid and rectum, with removal of the
pelvic colon, mesocolon, and adjacent lymph nodes, and wide
perineal excision of the rectum and anus, and a permanent
colostomy. |
|
Millin operation, a formerly
common method of radical retropubic prostatectomy. |
|
minor operation, an operation of
minor surgery (q.v.). |
|
Mitchell operation, a procedure for
correction of hallux valgus, involving distal osteotomy of the
first metatarsal. |
|
Motais operation, an operation for ptosis,
consisting of transplanting the middle portion of the tendon of
the superior rectus muscle of the eyeball into the upper lid. |
|
Mules operation, evisceration of the
eyeball, with insertion of artificial vitreous. |
|
Mustard operation, correction of
transposition of great vessels by construction of an
intra-atrial baffle, composed of pericardial tissue or synthetic
material, to direct the systemic and pulmonary venous blood into
the left and right ventricles, respectively. |
|
Naffziger operation, excision of the
superior and lateral walls of the orbit for exophthalmos. |
|
Nissen operation, see under
fundoplication. |
|
Ober operation, medial subtalar syndesmotomy
for clubfoot. |
|
Olshausen operation, the operation of fixing
or suturing the uterus to the abdominal wall for the cure of
retroversion. |
|
Ombrédanne operation,
transscrotal orchiopexy. |
|
open operation, an operation in which the
tissues and organs are exposed to view through a surgical
incision. |
|
Partsch operation, a technique for
marsupialization of dental cyst. |
|
Patey operation, modified radical
mastectomy. |
|
Péan operation, hip joint amputation in
which the vessels are ligated during the course of the
operation. |
|
Phelps operation, an open and direct
incision through the sole and inner side of the foot, done for
talipes. |
|
Phemister operation, use of an onlay graft
of cancellous bone without internal fixation, for treatment of a
stable but ununited fracture. |
|
plastic operation, one in which the shape of
a part or the character of its covering is altered by
transplantation of tissue or other means. |
|
Polya operation, subtotal
gastrectomy with anastomosis of the transected end of the
stomach to the side of the jejunum. |
|
Pomeroy operation, see under
technique. |
|
Potts operation, anastomosis between the
descending aorta and left pulmonary artery as palliative
treatment of congenital pulmonary stenosis. Called also Potts
anastomosis or shunt. |
|
pull-through operation, surgery on the
intestine in which a diseased segment is removed and a proximal
segment is pulled down and through the part just beyond the
removed part. See ileoanal pull-through anastomosis, Duhamel o.,
Soave o., and Swenson o. |
|
radical operation, see under
surgery. |
|
Ramstedt operation,
pyloromyotomy. |
|
Rastelli operation, an operation for
correction of large ventricular septal defects with pulmonary
infundibular and valvular stenosis; an intraventricular patch is
placed so that blood flows through the septal defect and out the
aorta, and a prosthesis is placed to establish continuity
between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery. |
|
Regnoli operation, excision of the tongue
through a median opening below the lower jaw, reaching from the
chin to the hyoid bone. |
|
Ridell operation, obliteration of the
frontal sinus by removal of the anterior wall and floor and
sometimes posterior walls of the sinus; for treatment of
malignant tumors. |
|
Roux-en-Y operation, see under
anastomosis. |
|
Saemisch operation, transfixion of the
cornea and of the base of the ulcer for the cure of hypopyon. |
|
Scanzoni operation, see under
maneuver. |
|
Schauta operation, radical hysterectomy by
the vaginal route. |
|
Schede operation, resection of the thorax
for chronic empyema.in cases of necrotic bone, excision of dead
bone and diseased tissue, after which the cavity is permitted to
fill with a blood clot that is kept moist and aseptic and
eventually becomes organized. |
|
Scheie operation, scleral cauterization with
peripheral iridectomy for treatment of glaucoma.a technique for
needling and aspiration of cataract. |
|
Sédillot operation, a flap operation for
restoring the upper lip. |
|
Senning operation, surgical creation of two
interatrial channels for crossing the systemic and pulmonary
venous circulations in transposition of the great vessels. |
|
Shirodkar operation, an operation for
incompetent cervix in which the cervical os is closed with a
surrounding purse-string suture. |
|
Silver operation, resection of the medial
prominence of the first metatarsal head, medial capsulorrhaphy
of the first metatarsophalangeal joint, and sectioning of the
adductor tendon; done for hallux valgus. |
|
Sistrunk operation, a surgical procedure for
removal of thyroglossal cysts and sinuses. |
|
Smith operation, extraction of an immature
cataract with an intact capsule. |
|
Soave operation, treatment of congenital
megacolon by an endorectal pull-through operation, with normal
colon connected to the anus through a rectum denuded of mucosa.
See illustration. |
|
Spinelli operation, the operation of
splitting the anterior wall of the prolapsed inverted uterus,
reversing the organ, and restoring it to the correct position. |
|
Ssabanejew-Frank operation, a
formerly common type of gastrostomy with suture of the stomach
to the body wall. |
|
Stein operation, an operation for
reconstruction of the lower lip with flaps taken from the upper
lip. |
|
Steindler operation, surgical correction of
pes cavus by stripping muscle and fascia from the plantar
calcaneal surface. |
|
Stokes operation, Gritti-Stokes
amputation. |
|
Strömbeck operation, see under
mammaplasty. |
|
Sturmdorf operation, conical excision of the
diseased endocervix. |
|
Swenson operation, an operation for
congenital megacolon, consisting of removal of the rectum and
the aganglionic segment of the intestine and an ileoanal
pull-through anastomosis with preservation of the anal
sphincters. See illustration. |
|
|
|
Operations to remove or counterbalance the obstructive effect of
the aganglionic segment in congenital megacolon. The Swenson
operation removes the segment up to the dentate line
posteriorly, leaving a short segment of abnormal bowel
anteriorly. The Duhamel operation excises the aganglionic
segment above the peritoneal reflection only. The Soave
operation is an endorectal mucosal proctectomy with the rectal
muscle layer left in place. |
|
|
Syme operation, see under
amputation. |
|
tagliacotian operation, see under
rhinoplasty. |
|
Tanner operation, an operation
for bleeding esophageal varices in which the terminal end of the
esophagus and the proximal part of the stomach are freed of
external vascular and ligamentous connections, and the stomach
is transected below the cardia. |
|
Teale operation, see under
amputation. |
|
Thiersch operation, removal of thin
split-thickness skin grafts by means of a razor, skin-graft
cutting knife, or a dermatome. |
|
Thompson operation, a formerly
common treatment for elephantiasis and other types of massive
lymphedema of the lower limb, consisting of excision of some
subcutaneous tissue and burying of a dermal flap among the
underlying muscles. |
|
Torek operation, one of the pioneering
operations for esophageal cancer, consisting of removal of the
thoracic part of the esophagus. |
|
Torkildsen operation,
ventriculocisternal shunt. |
|
Toti operation,
dacryocystorhinostomy. |
|
Toupet operation, see under
fundoplication. |
|
Trendelenburg operation, an early
method for treating varicose veins, consisting of ligation of
the great saphenous vein.synchondroseotomy.transthoracic
pulmonary embolectomy. |
|
van Hook operation,
ureteroureterostomy. |
|
Vineberg operation, implantation of the
internal mammary artery into the myocardium to enhance the
growth of collateral circulation. |
|
Vladimiroff operation, Mikulicz
o. (def. 3). |
|
von Burow operation, Burow o. |
|
Waters operation, a form of extraperitoneal
cesarean section. |
|
Waterston operation, anastomosis between the
ascending aorta and right pulmonary artery as palliative
treatment of congenital pulmonary stenosis. Called also
Waterston anastomosis or shunt. |
|
Watkins operation, an operation
for prolapse and procidentia uteri in which the bladder is
separated from the anterior wall of the uterus so that the
uterus is left in a position to support the entire bladder.
Called also interposition o. |
|
Webster operation, for retrodisplacement of
the uterus: the round ligaments are passed through the
perforated broad ligaments and fixed to the back of the uterus. |
|
Wertheim operation, radical hysterectomy;
removal of the uterus, tubes, parametrium, tissues surrounding
the upper vagina, and pelvic lymphatics. |
|
Whipple operation, see under
procedure. |
|
Whitehead operation, a treatment
for hemorrhoids consisting of surgical removal. |
|
Whitman operation, an operation for
arthroplasty of the hip joint.a method of astragalectomy. |
|
Witzel operation, see under
gastrostomy. |
|
Young operation, an operation for penile
epispadias, with formation of a new urethral tube.perineal
prostatectomy. |
|
Ziegler operation, V-shaped iridectomy for
forming an artificial pupil. |
|
|

