| CRANIAL SUTURES |
| HEMOSTATIC SUTURES |
| SUTURES OF THE SKULL |
| 1. sutura. |
| 2. a loop of thread, catgut, or similar material used to secure apposition of the edges of a surgical or accidental wound; called also stitch. See Plate 47. |
| 3. to unite the edges of a wound using such loops; called also stitch. |
| 4. the material used in thus closing a wound; see absorbable s. and nonabsorbable s |
| absorbable suture, a surgical suture that closes a wound and later either is digested by proteolytic enzymes derived from inflammatory cells or is hydrolyzed by water. |
| absorbable surgical suture, a sterile absorbable suture made of collagen derived from healthy mammals or from a synthetic polymer, available in various diameters and tensile strengths; it may be treated to modify its resistance to absorption, impregnated with a suitable antimicrobial agent, and colored. |
| Albert suture, a form of Czerny suture in which the first row of stitches is passed through the entire thickness of the intestine. |
| apposition suture, a superficial suture used for bringing together the cutaneous edges of a wound. |
| approximation suture, a deep suture for bringing together the deep tissues of a wound. |
| arcuate suture, sutura coronalis. |
| atraumatic suture, a suture fused into the end of a small eyeless needle. |
| basilar suture, fissura sphenooccipitalis. |
| Bell suture, a form of lock-stitch in which the needle is passed from within outward alternately on the two edges of the wound. |
| biparietal suture, sutura sagittalis. |
| bolster suture, a suture the ends of which are tied over a tiny roll of gauze or a piece of rubber tubing, in order to lessen the pressure on the skin. |
| bony suture, sutura. |
| bregmatomastoid suture, sutura parietomastoidea. |
| Bunnell suture, a figure-of-eight zigzag suture used for tendon repair. |
| buried suture, one that is placed deep in the tissues and concealed by the skin. |
| button suture, one in which the stitch is passed through a button-like disk to prevent the suture material from cutting through the skin. |
| catgut suture, see surgical gut, under gut. |
| chain suture, a continuous suture in which each loop of thread is caught by the next adjacent loop. |
| circular suture, one that is applied to the entire circumference of a hollow viscus to secure closure, or to a portion of a visceral wall to achieve inversion of the enclosed circular area. |
| coaptation suture, apposition s. |
| cobbler's suture, double-armed s. |
| collagen suture, a suture made from the tendons of cattle, chemically treated, purified, and processed into strands; it is most often used in ophthalmologic surgery. |
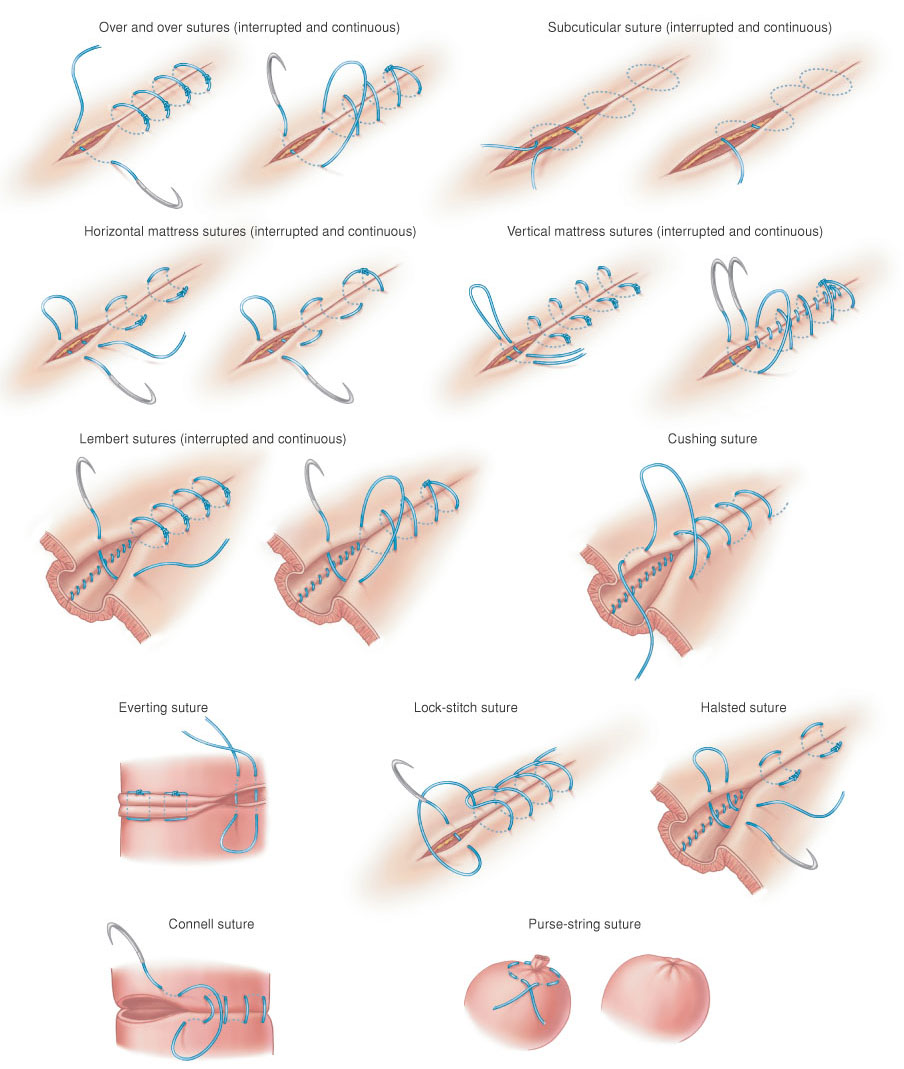
| Connell suture, a U-shaped continuous suture used in intestinal anastomosis, the stitches being placed parallel to and about 4 mm from the edge of the wound, and passing through all the layers of the intestinal wall. See Plate 47. |
| continuous suture, one in which a continuous, uninterrupted length of material is used to approximate the cut edges of one or more layers of tissues. |
| coronal suture, sutura coronalis. |
| cranial sutures, suturae cranii. |
| Cushing suture, a type of continuous inverting suture used for closing the seromuscular layers in surgery of the gastrointestinal tract. See Plate 47. |
| Czerny suture, an intestinal suture in which the thread is passed through the mucous membrane alone.a method of uniting a ruptured tendon by splitting one of the ends and suturing the other end into the slit. |
| Czerny-Lembert suture, a combination of Czerny and Lembert sutures in circular enterorrhaphy. |
| dentate suture, sutura serrata. |
| double-armed suture, one made with suture material threaded through a needle at each end. Called also cobbler's suture. |
| double-button suture, a form of stitch in which the suture material is passed deep across the edges of the wound, between two buttons placed on the surface of the skin, one on either side of the suture line. |
| Dupuytren suture, a continuous Lembert suture. |
| ethmoidomaxillary suture, sutura ethmoidomaxillaris. |
| everting suture, a method by which the approximated edges of a wound are turned outward; formed by encircling with the needle a larger amount of tissue at the depth of the wound than at the periphery. See Plate 47. |
| false suture, sutura plana. |
| figure-of-eight suture, one in which the thread follows the contours of the figure 8. |
| flat suture, sutura plana. |
| frontal suture, sutura frontalis.sutura frontalis persistens. |
| frontoethmoidal suture, sutura frontoethmoidalis. |
| frontolacrimal suture, sutura frontolacrimalis. |
| frontomaxillary suture, sutura frontomaxillaris. |
| frontonasal suture, sutura frontonasalis. |
| frontoparietal suture, sutura coronalis. |
| frontosphenoid suture, sutura sphenofrontalis. |
| frontozygomatic suture, sutura frontozygomatica. |
| Gaillard-Arlt suture, a suture used in correction of entropion. |
| Gély suture, a type of continuous suture used for repair of intestinal wounds, made by a thread with a needle at each end, and consisting of a series of cross-stitches closing the wound. |
| glover's suture, lock-stitch s. |
| suture of Goethe, sutura incisiva. |
| Gussenbauer suture, a pioneering type of figure-of-eight suture that was used in intestinal surgery. |
| Halsted suture, a modification of the Lembert suture, consisting of a stitch parallel to the wound on one side, with the two free ends of the material emerging on the other side, where they are tied. See Plate 47. |
| harelip suture, a figure-of-eight suture used in the correction of cleft lip. |
| hemostatic sutures, sutures used to control oozing of blood from raw areas. |
| incisive suture, sutura incisiva. |
| infraorbital suture, sutura zygomaticomaxillaris. |
| intermaxillary suture, sutura intermaxillaris. |
| internasal suture, sutura internasalis. |
| interparietal suture, sutura sagittalis. |
| interrupted suture, a noncontinuous suture; one in which each stitch is made with a separate piece of material. |
| intradermic suture, a suture applied parallel with the edges of the wound, but within the layers of the skin, usually a continuous stitch. |
| inverting suture, a type used in intestinal anastomosis to appose and invert the serosal surfaces of the two segments, as in Cushing sutures and Lembert sutures. |
| jugal suture, sutura sagittalis. |
| lacrimoconchal suture, sutura lacrimoconchalis. |
| lacrimoethmoidal suture, sutura ethmoidolacrimalis. |
| lacrimomaxillary suture, sutura lacrimomaxillaris. |
| lambdoid suture, sutura lambdoidea. |
| Le Dentu suture, a type used for a divided tendon; two stitches are passed on each side, right and left, and are tied in front, and a third is taken from right to left above and below the cut and is tied on one side. |
| Le Fort suture, for a divided tendon: a single loop is passed above the cut, entering at one side, coming out and going in at the front; it is then passed below the cut at each side, coming out in front, and is there tied. |
| Lembert suture, a type of inverting suture commonly used in gastrointestinal surgery. The needle is inserted a short distance away from the incision, brought through the serous and muscular coats but not the submucosa, and brought out near the edge of the incision; then it is inserted near the edge on the opposite side and brought out at a more distant point without entering the lumen of the intestine. These sutures may be either interrupted or continuous. See Plate 47. |
| limbous suture, sutura limbosa. |
| lock-stitch suture, a continuous hemostatic suture used in intestinal surgery. The needle is passed through all layers of the intestinal wall and the suture loop is made to fall over the point where the needle emerges from the skin; this forms a self-locking stitch when the strand is pulled taut. See Plate 47. |
| longitudinal suture, sutura sagittalis. |
| loop suture, interrupted s. |
| mammillary suture, mastoid suture, sutura occipitomastoidea. |
| mattress suture, horizontal, a method in which the stitches are made parallel with the edges of the wound, the suture material crossing deeply from one side to the other. See Plate 47. |
| mattress suture, right-angle, mattress s., vertical. |
| mattress suture, vertical, a method in which the stitches are made at right angles to the edges of the wound, taking both deep and superficial bites of tissue, the latter achieving more exact apposition of the cutaneous margins. See Plate 47. |
| metopic suture, sutura frontalis persistens. |
| nasofrontal suture, sutura frontonasalis. |
| nasomaxillary suture, sutura nasomaxillaris. |
| nerve suture, neurorrhaphy. |
| nonabsorbable suture, material for closing wounds which is not absorbed in the body, e.g., silk, cotton, and stainless steel, or synthetic material such as nylon. |
| nonabsorbable surgical suture, a strand of material resistant to the action of living mammalian tissue, available in various diameters and tensile strengths. There are three types: Class I is composed of monofilament, twisted, or braided silk or synthetic fibers; if there is a coating, it does not significantly affect the thickness. Class II is composed of cotton or linen fibers or of coated natural or synthetic fibers having a coating that significantly affects the thickness but not the strength. Class III is monofilament or multifilament wire. |
| occipital suture, sutura lambdoidea. |
| occipitomastoid suture, sutura occipitomastoidea. |
| occipitoparietal suture, sutura lambdoidea. |
| occipitosphenoidal suture, fissura sphenooccipitalis. |
| over-and-over suture, a method in which equal bites of tissue are taken on each side of the wound; it may be either interrupted or continuous. See Plate 47. |
| palatine suture, anterior, sutura incisiva. |
| palatine suture, median, palatine suture, middle, sutura palatina mediana. |
| palatine suture, transverse, sutura palatina transversa. |
| palatoethmoidal suture, sutura palatoethmoidalis. |
| palatomaxillary suture, sutura palatomaxillaris. |
| Pancoast suture, a form of tongue-and-groove suture; see plastic s. |
| Paré suture, the use of strips of cloth applied along the edges of a wound, and then stitched together to bring the margins of the wound into apposition. |
| parietal suture, sutura sagittalis. |
| parietomastoid suture, sutura parietomastoidea. |
| parietooccipital suture, sutura lambdoidea. |
| petrobasilar suture, petrosphenobasilar suture, synchondrosis petrooccipitalis. |
| petrosphenooccipital suture of Gruber, fissura petrooccipitalis. |
| petrosquamous suture, fissura petrosquamosa. |
| plastic suture, a method in which a tongue is cut in one lip of the wound and a groove in the other, the tongue and groove then being stitched together, and the ends of the thread tied over a roll of adhesive plaster. |
| premaxillary suture, sutura incisiva. |
| presection suture, a stitch or series of stitches placed in the tissues before an incision is made. |
| primary suture, prompt surgical closure of a wound. |
| purse-string suture, a continuous suture placed around a circular opening that is to be inverted; commonly used for the stump of the appendix or a hernia sac. See Plate 47. |
| quilt suture, quilted suture, a continuous mattress suture. |
| relaxation suture, any suture placed to close a wound but so formed that it may be loosened in order to relieve the tension should it become too great. |
| retention suture, a reinforcing suture for abdominal wounds, utilizing exceptionally strong material like braided silk or stainless steel, and including a large amount of tissue in each stitch; intended to relieve pressure on the primary suture line and prevent postoperative wound disruption or evisceration. |
| rhabdoid suture, sutura sagittalis. |
| sagittal suture, sutura sagittalis. |
| secondary suture, delayed closure of an operative or accidental wound, usually because of the presence or expectation of infection.resuture of an operative wound following disruption. |
| seroserous suture, a suture that brings together two serous surfaces. |
| serrated suture, sutura serrata. |
| shotted suture, Sims suture, one in which the two ends of the suture wire are passed through a split or perforated lead shot, which is then compressed. |
| sutures of skull, suturae cranii. |
| sphenoethmoidal suture, sutura sphenoethmoidalis.a craniometric landmark, being the most superior point of the sutura sphenoethmoidalis. Called also point SE. Abbreviated SE. |
| sphenofrontal suture, sutura sphenofrontalis. |
| sphenomaxillary suture, sutura sphenomaxillaris. |
| sphenooccipital suture, fissura sphenooccipitalis. |
| sphenoorbital suture, sutura sphenoorbitalis. |
| sphenoparietal suture, sutura sphenoparietalis. |
| sphenopetrosal suture, synchondrosis petrooccipitalis. |
| sphenosquamous suture, sphenotemporal suture, sutura sphenosquamosa. |
| sphenovomerine suture, sutura sphenovomeralis. |
| sphenozygomatic suture, sutura sphenozygomatica. |
| squamomastoid suture, squamosomastoid suture, sutura squamomastoidea. |
| squamosoparietal suture, sutura squamosa cranii. |
| squamososphenoid suture, sutura sphenosquamosa. |
| squamous suture, sutura squamosa. |
| squamous suture of cranium, sutura squamosa cranii. |
| subcuticular suture, a method of skin closure involving placement of stitches in the subcuticular tissues parallel with the line of the wound; continuous or interrupted sutures may be used. See Plate 47. |
| superficial suture, one that is placed through the superficial fascia only. |
| temporal suture, sutura squamosa cranii. |
| temporozygomatic suture, sutura temporozygomatica. |
| tongue-and-groove suture, plastic s. |
| transverse suture of Krause, sutura zygomaticomaxillaris. |
| true suture, sutura. |
| uninterrupted suture, continuous s. |
| zygomaticofrontal suture, sutura frontozygomatica. |
| zygomaticomaxillary suture, sutura zygomaticomaxillaris. |
| zygomaticotemporal suture, sutura temporozygomatica. |