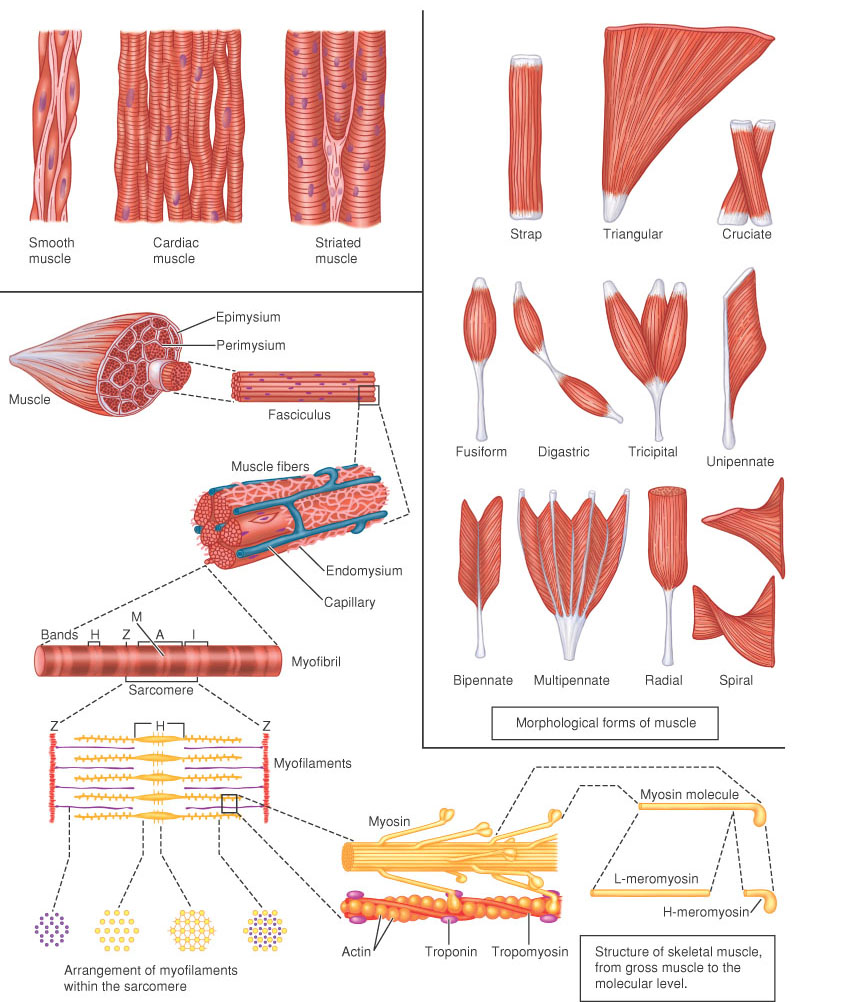
| coracobrachialis | coracobrachial muscle: origin, coracoid process of scapula; insertion, medial surface of shaft of humerus; innervation, musculocutaneous nerve; action, flexes, adducts arm. |
| brachialis | brachial muscle: origin, anterior surface of humerus; insertion, coronoid process of ulna; innervation, radial, musculocutaneous nerve; action, flexes forearm. |
| hypothenar | the intrinsic muscles of the little finger; flexing, abducting, and opposing it, and consisting of the palmaris brevis, abductor digiti minimi, flexor digiti minimi brevis, and opponens digiti minimi muscles. |
| palmar aponeurosis | Palmar aponeurosis. A fifth longitudinal band, radiating toward the base of the thumb, is sometimes present. |
| abductor pollicis brevis | short abductor muscle of thumb: origin, scaphoid, ridge of trapezium, flexor retinaculum of hand; insertion, lateral surface of base of proximal phalanx of thumb; innervation, median nerve; action, abducts thumb |
| flexor retinaculum | a fibrous band forming the carpal tunnel, through which pass the tendons of the flexor muscles of the hand and fingers |
| palmaris longus | origin, medial epicondyle of humerus; insertion, flexor retinaculum of hand, palmar aponeurosis; innervation, median nerve; action, flexes wrist joint, anchors skin and fascia of hand. |
| flexor carpi radialis | radial flexor muscle of wrist: origin, medial epicondyle of humerus; insertion, base of second metacarpal; innervation, median nerve; action, flexes and abducts wrist joint. |
| brachioradials | |
| biceps | a muscle having two heads. The biceps muscle of the upper limb flexes and supinates the forearm; the biceps muscle of the thigh flexes and rotates the lower limb laterally and extends the thigh. |
| triceps | a muscle having three heads |
| flexor carpi ulnaris | ulnar flexor muscle of wrist (2 heads): origin,HUMERAL HEAD—medial epicondyle of humerus, ULNAR HEAD—olecranon, ulna, intermuscular septum; insertion, pisiform bone, hook of hamate bone, proximal end of fifth metacarpal bone; innervation, ulnar nerve; action, flexes and adducts wrist joint. |
| flexor digitorum superficialis | superficial flexor muscle of fingers (2 heads): origin,HUMEROULNAR HEAD—medial epicondyle of humerus, coronoid process of ulna, RADIAL HEAD— oblique line of radius, anterior border; insertion, sides of middle phalanges of four (nonthumb) fingers; innervation, median nerve; action, primarily flexes middle phalanges |
| supinate | the act of turning the palm forward or upward, or of raising the medial margin of the foot. |
| supination | the act of assuming the supine position; placing or lying on the back. Applied to the hand, the act of turning the palm upward |
| pronate | to subject to pronation |
| pronation | the act of assuming the prone position, or the state of being prone. Applied to the hand, turning the palm backward (posteriorly) or downward, performed by medial rotation of the forearm. Applied to the foot, a combination of eversion and abduction movements taking place in the tarsal and metatarsal joints and resulting in lowering of the medial margin of the foot, hence of the longitudinal arch |
| flex | to bend or put in a state of flexion |
| flexion | the act of bending or the condition of being bent. |
| extend | in obstetrics, the normal bending forward of the head of the fetus in the uterus or birth canal so that the chin rests on the chest, thereby presenting the smallest diameter of the vertex |
| digits | a finger or toe. adj., dig´ital., adj. |
| pollex | Latin word meaning thumb;; a term used in anatomy. |
| Pollex Valgus | deviation of the thumb toward the ulnar side |
| Pollex Varus | deviation of the thumb toward the radial side |
| anconeus | origin, back of lateral epicondyle of humerus; insertion, olecranon and posterior surface of ulna; innervation, radial nerve; action, extends forearm. |
| extensor digiti minimi | extensor muscle of little finger: origin, common extensor tendon and adjacent intermuscular septa; insertion, extensor expansion of little finger; innervation, deep branch of radial nerve; action, extends little finger. |
| extensor digitorum muscle | extensor muscle of fingers: origin, lateral epicondyle of humerus; insertion, extensor expansion of each (nonthumb) finger; innervation, posterior interosseus nerve; action, extends wrist joint and phalanges. |
| extensor digitorum Communis | |
| flexor pollicis longus | long flexor muscle of thumb: origin, anterior surface of radius, interosseous membrane, and medial epicondyle of humerus or coronoid process of ulna; insertion, base of distal phalanx of thumb; innervation, anterior interosseous nerve; action, flexes thumb. |
| pronator teres | (2 heads): origin,HUMERAL HEAD—medial epicondyle of humerus, ULNAR HEAD—coronoid process of ulna; insertion, lateral surface of radius; innervation, median nerve; action, flexes elbow and pronates forearm. |
| epicondyle | an eminence upon a bone, above its condyle. |
| pronator quadratus | origin, anterior surface and border of distal third or fourth of shaft of ulna; insertion, anterior surface and border of distal fourth of shaft of radius; innervation, anterior interosseous nerve; action, pronates forearm |
| supinator | origin, lateral epicondyle of humerus, ulna, elbow joint fascia; insertion, radius; innervation, deep radial nerve; action,supinates forearm. |
| retinaculum | a structure that retains an organ or tissue in place. |
| thenar muscle | the abductor and flexor muscles of the thumb |
| thenar | the fleshy part of the hand at the base of the thumb |
| apneurosis | pl. aponeuro´ses a sheetlike tendinous expansion, mainly serving to connect a muscle with the parts it moves. adj., aponeurot´ic., adj. |
| longus | Latin word meaning long; a term used in anatomy. |
| bevis | |
| radials | radiating; spreading outward from a common center. pertaining to a radius. |
| ulnaris | Latin word meaning pertaining to the ulna, ulnar;. A term used in anatomy. |
| flexor retinaculum - retinacula | a fibrous band forming the carpal tunnel, through which pass the tendons of the flexor muscles of the hand and fingers |
LEGS
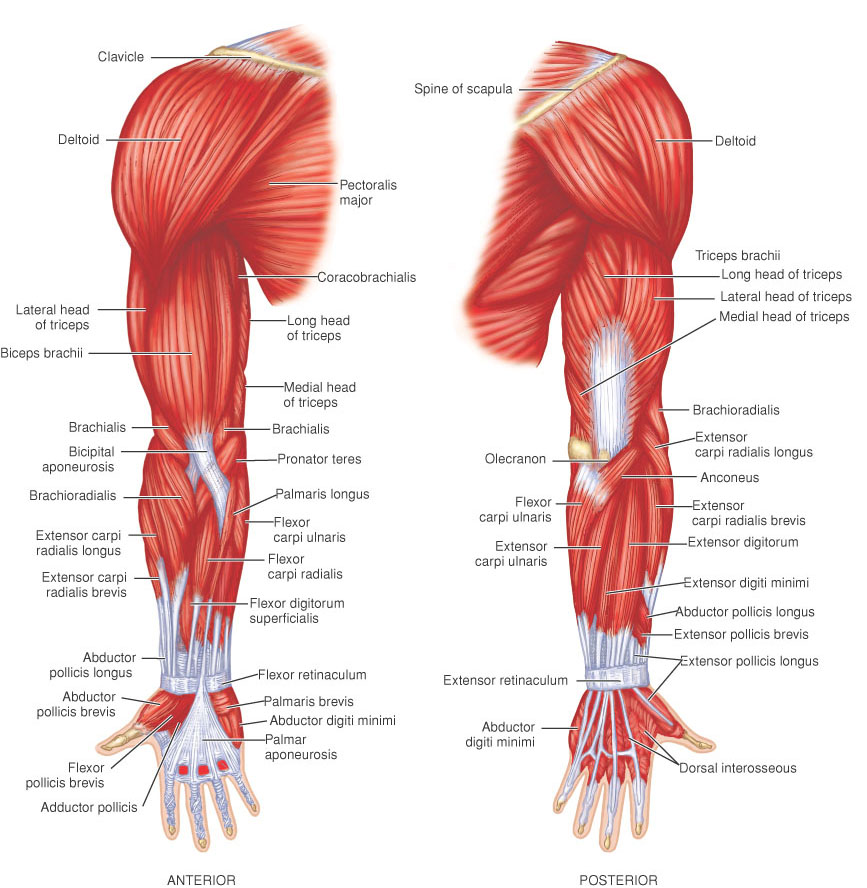
| Tensor fasciae latae | origin, iliac crest; insertion, iliotibial tract of fascia lata; innervation, superior gluteal nerve; action, flexes, rotates thigh medially. |
| Sartorius | origin, anterior superior iliac spine; insertion, proximal part of medial surface of tibia; innervation, femoral nerve; action, flexes leg at knee and thigh at pelvis. |
| rectus femoris | origin, anterior inferior iliac spine, rim of acetabulum; insertion, base of patella, tuberosity of tibia; innervation, femoral nerve; action, extends knee, flexes thigh at hip. |
| vastus lateralis | origin, lateral aspect of femur; insertion, patella, common tendon of quadriceps femoris muscle; innervation, femoral nerve; action, extends leg. |
| peroneus longus | long peroneal muscle: origin, lateral condyle of tibia, head and lateral surface of fibula; insertion, medial cuneiform bone, first metatarsal bone; innervation, superficial peroneal nerve; action, abducts, everts, plantar flexes foot. |
| peroneus brevis | short peroneal muscle: origin, lateral surface of fibula; insertion, tuberosity on base of fifth metatarsal bone; innervation, superficial peroneal nerve; action, everts, abducts, plantar flexes foot. |
| lateral malleolus - Medial (Middle) malleolus |
a rounded process.either of the two rounded prominences on
either side of the ankle joint; the lateral (or fibular,
external, or outer) malleolus is at the lower end of the fibula
and the medial (or tibial, internal, or inner) malleolus is at
the lower end of the tibia. adj. malle´olar., adj. |
| extensor digitorum longus | long extensor muscle of toes: origin, anterior surface of fibula, lateral condyle of tibia, interosseous membrane; insertion, extensor expansion of each of the four lateral toes: innervation, deep peroneal nerve; action, extends toes. |
| adductor magnus | great adductor muscle (2 parts): origin,DEEP PART—inferior ramus of pubis, ramus of ischium, SUPERFICIAL PART—ischial tuberosity; insertion,DEEP PART—linea aspera of femur, SUPERFICIAL PART—adductor tubercle of femur; innervation,DEEP PART—obturator nerve, SUPERFICIAL PART—sciatic nerve; action,DEEP PART—adducts thigh, SUPERFICIAL PART—extends thigh |
| semitendinosus | semitendinous muscle: origin, tuberosity of ischium; insertion, upper part of medial surface of tibia; innervation, tibial nerve; action, flexes and rotates leg medially, extends thigh. |
| semimembranosus | semimembranous muscle: origin, tuberosity of ischium; insertion, medial condyle and border of tibia, lateral condyle of femur; innervation, tibial nerve; action, flexes and rotates leg medially, extends thigh at hip. |
| Calcaneal (Achilles) Tendon BURSA | a bursa between the calcaneal tendon and the back of the calcaneus. |
| iliopsoas | a compound muscle consisting of the iliacus and the psoas major muscles. |
| pectineus | pectineal muscle: origin, pectineal line of pubis; insertion, pectineal line of femur; innervation, obturator and femoral nerves; action, flexes, adducts thigh |
| adductor longus | long adductor muscle: origin, crest and symphysis of pubis; insertion, linea aspera of femur; innervation, obturator nerve; action, adducts, rotates, flexes thigh. |
| gracilis | origin, body and inferior ramus of pubis; insertion, medial surface of shaft of tibia; innervation, obturator nerve; action, adducts thigh, flexes knee joint. |
| vastus medialis | origin, medial aspect of femur; insertion, patella, common tendon of quadriceps femoris muscle; innervation, femoral nerve; action, extends leg |
| gastrocnemius | origin,MEDIAL HEAD—popliteal surface of femur, upper part of medial condyle, and capsule of knee, LATERAL HEAD—lateral condyle and capsule of knee; insertion, aponeurosis unites with tendon of soleus to form Achilles tendon; innervation, tibial nerve; action, plantar flexes ankle joint, flexes knee joint |
| soleus | origin, fibula, tibia, tendinous arch between tibia and fibula and passing over popliteal vessels; insertion, calcaneus by Achilles tendon; innervation, tibial nerve; action, plantar flexes foot. |
| extensor retinaculum | a fibrous band forming the carpal tunnel, through which pass the tendons of the flexor muscles of the hand and fingers |
| anterior tibial | veins that follow the course of the anterior tibial artery. They unite with the posterior tibial veins to form the popliteal vein. |
| gastrocnemius | origin,MEDIAL HEAD—popliteal surface of femur, upper part of medial condyle, and capsule of knee, LATERAL HEAD—lateral condyle and capsule of knee; insertion, aponeurosis unites with tendon of soleus to form Achilles tendon; innervation, tibial nerve; action, plantar flexes ankle joint, flexes knee joint |
| extensor hallucis longus | long extensor muscle of great toe: origin, front of fibula and interosseous membrane; insertion, base of distal phalanx of great toe; innervation, deep peroneal nerve; action, dorsiflexes ankle joint, extends great toe. |
| gluteus maximus | origin, posterior aspect of ilium, posterior surface of sacrum and coccyx, sacrotuberous ligament, fascia covering gluteus medius muscle; insertion, iliotibial tract of fascia lata, gluteal tuberosity of femur; innervation, inferior gluteal nerve; action, extends, abducts, and rotates thigh laterally. |
| greater trochanter | either of two broad, flat processes on the femur. The greater trochanter is at the upper end of the bone's lateral surface, and the lesser trochanter is a short conical process on the posterior border of the neck of the femur. adj., trochanter´ic, trochanter´ian., adj. |
| iliotibial tract | a thickened longitudinal band of fascia lata extending from the tensor muscle downward to the lateral condyle of the tibia |
| biceps | a muscle having two heads. The biceps muscle of the upper limb flexes and supinates the forearm; the biceps muscle of the thigh flexes and rotates the lower limb laterally and extends the thigh. |
| peroneous longus | long peroneal muscle: origin, lateral condyle of tibia, head and lateral surface of fibula; insertion, medial cuneiform bone, first metatarsal bone; innervation, superficial peroneal nerve; action, abducts, everts, plantar flexes foot. |
| peroneus bevis | short peroneal muscle: origin, lateral surface of fibula; insertion, tuberosity on base of fifth metatarsal bone; innervation, superficial peroneal nerve; action, everts, abducts, plantar flexes foot |
TORSO
| ANTERIOR | |
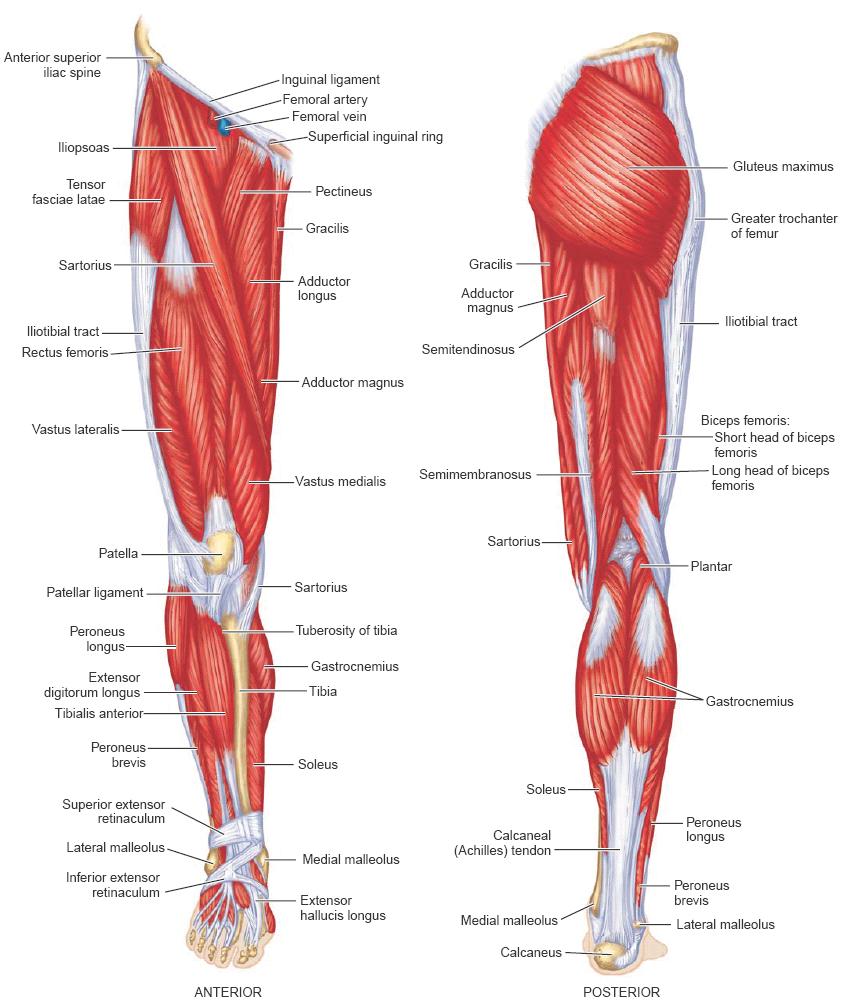
| Trapezius | origin, occipital bone, nuchal ligament, spinous processes of seventh cervical and all thoracic vertebrae; insertion, clavicle, acromion, spine of scapula; innervation, accessory nerve and cervical plexus; action, elevates shoulder, rotates scapula to raise shoulder in abduction of arm, draws scapula backward |
| deltoid | origin, clavicle, acromion, spine of scapula; insertion, deltoid tuberosity of humerus; innervation, axillary nerve; action, abducts, flexes, extends arm. It is the muscular cap of the shoulder, and is often used as a site for an intramuscular injection. |
| pectoralis major | greater pectoral muscle: origin, clavicle, sternum, six upper costal cartilages, aponeurosis of external oblique muscle of abdomen; the origins are reflected in the subdivision of the muscle into clavicular, sternocostal, and abdominal parts; insertion, crest of intertubercular groove of humerus; innervation, medial and lateral pectoral nerves; action, adducts, flexes, rotates arm medially |
| serratus anterior | origin, eight or nine upper ribs; insertion, medial border of scapula; innervation, long thoracic nerve; action, draws scapula forward; rotates scapula to raise shoulder in abduction of arm. |
| sternocleidomastoid | (2 heads): origin,STERNAL HEAD—manubrium sterni, CLAVICULAR HEAD—superior surface of medial third of clavicle; insertion, mastoid process and superior nuchal line of occipital bone; innervation, accessory nerve and cervical plexus; action, flexes vertebral column, rotates head upward and to opposite side |
| external oblique | origin, lower eight ribs at costal cartilages; insertion, crest of ilium, linea alba through rectus sheath; innervation, seventh to twelfth intercostal nerves; action, flexes and rotates vertebral column, increases intra-abdominal pressure, acts as accessory respiratory muscle. |
| rectus abdominis | origin, pubic crest and symphysis; insertion, xiphoid process, cartilages of fifth, sixth, and seventh ribs; innervation, branches of lower thoracic nerves; action, flexes lumbar vertebrae, supports abdomen |
| Not Muscle: | |
| Linea Alba - | white line; the tendinous median line on the anterior abdominal wall between the two rectus muscles |
| Umbilicus | the (usually) depressed scar marking the site where the umbilical cord entered the fetus; called also navel |
| POSTERIOR | |
| Trapezius | origin, occipital bone, nuchal ligament, spinous processes of seventh cervical and all thoracic vertebrae; insertion, clavicle, acromion, spine of scapula; innervation, accessory nerve and cervical plexus; action, elevates shoulder, rotates scapula to raise shoulder in abduction of arm, draws scapula backward |
| infraspinatus | origin, infraspinous fossa of scapula; insertion, greater tubercle of humerus; innervation, suprascapular nerve; action, rotates humerus laterally |
| teres major | origin, inferior angle of scapula; insertion, lip of intertubercular sulcus of humerus; innervation, lower subscapular nerve; action, adducts, extends, rotates arm medially. |
| latissimus dorsi | origin, spines of lower thoracic vertebrae, lumbar and sacral vertebrae through attachment to thoracolumbar fascia, iliac crest, lower ribs, inferior angle of scapula; insertion, floor of intertubercular sulcus of humerus; innervation, thoracodorsal nerve; action, adducts, extends, and rotates humerus medially |
| gluteus maximus | origin, posterior aspect of ilium, posterior surface of sacrum and coccyx, sacrotuberous ligament, fascia covering gluteus medius muscle; insertion, iliotibial tract of fascia lata, gluteal tuberosity of femur; innervation, inferior gluteal nerve; action, extends, abducts, and rotates thigh laterally |
| rhomboideus | |
| supraspinatus | supraspinous muscle: origin, supraspinous fossa of scapula; insertion, greater tubercle of humerus; innervation, suprascapular nerve; action, abducts humerus. |
| iliocostalis dorsi | iliocostal muscle: the lateral division of the erector spinae muscle, which includes the iliocostalis cervicis, iliocostalis thoracis, and iliocostalis lumborum muscles. |
| deltoid | origin, clavicle, acromion, spine of scapula; insertion, deltoid tuberosity of humerus; innervation, axillary nerve; action, abducts, flexes, extends arm. It is the muscular cap of the shoulder, and is often used as a site for an intramuscular injection. |
| teres minor | origin, lateral margin of scapula; insertion, greater tubercle of humerus; innervation, axillary nerve; action, rotates arm laterally |
| lumbar aponeurosis - dorsolumbar fascia | lumbar - pl. aponeuro´ses a sheetlike tendinous expansion, mainly serving to connect a muscle with the parts it moves. adj., aponeurot´ic., adj. |
| gluteus medius | origin, lateral surface of ilium between anterior and posterior gluteal lines; insertion, greater trochanter of femur; innervation, superior gluteal nerve; action, abducts and rotates thigh medially |

HEAD
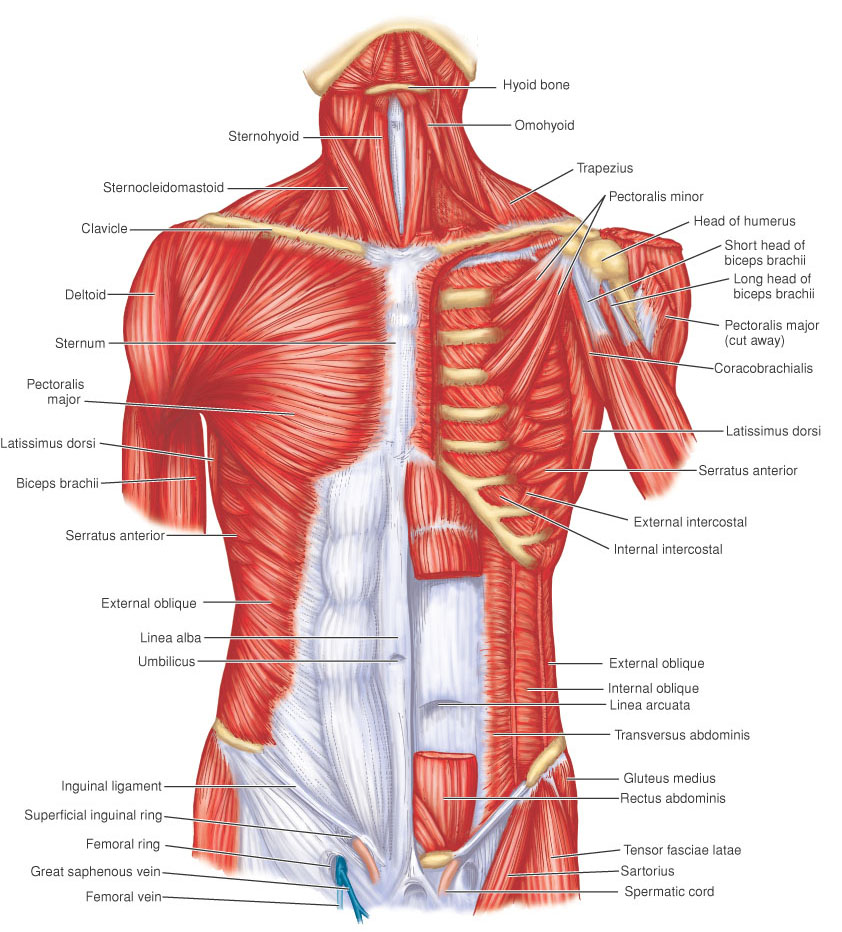
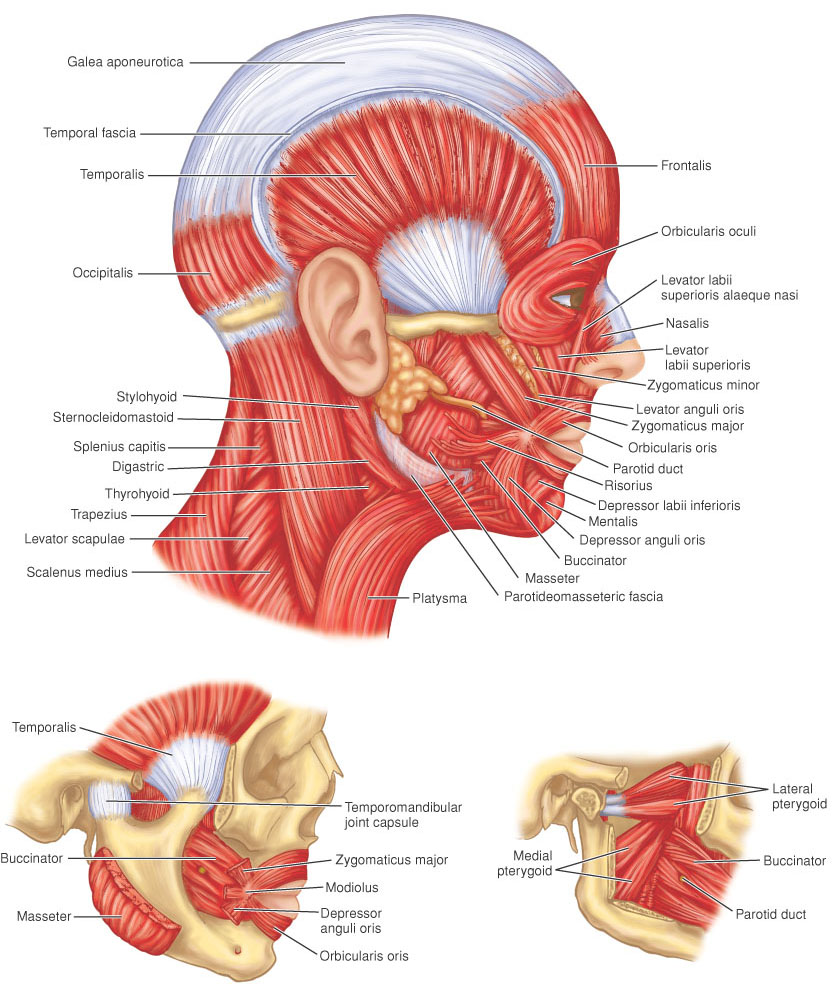
| frontalis | Latin word meaning related to the forehead, or frontal |
| temporalis | temporal muscle: origin, temporal fossa and fascia; insertion, coronoid process of mandible; innervation, mandibular nerve; action, closes jaws. |
| orbicularis Oculi | the oval sphincter muscle surrounding the eyelids, consisting of three parts: origin,ORBITAL PART—medial margin of orbit, including frontal process of maxilla, PALPEBRAL PART— medial palpebral ligament, LACRIMAL PART—posterior lacrimal crest; insertion,ORBITAL PART—near origin after encircling orbit, PALPEBRAL PART—fibers intertwine to form lateral palpebral raphe, LACRIMAL PART—lateral palpebral raphe, upper and lower tarsi; innervation, facial nerve; action, closes eyelids, wrinkles forehead, compresses lacrimal sac. |
| buccinator | origin, buccinator ridge of mandible, alveolar process of maxilla, pterygomandibular ligament; insertion, orbicularis oris muscle at angle of mouth; innervation, buccal branch of facial nerve; action, compresses cheek and pulls back angle of the mouth |
| orbicularis oris | a name applied to a complicated sphincter muscle of the mouth, consisting of a labial part, fibers restricted to the lips, and a marginal part, fibers blending with those of adjacent muscles; innervation, facial nerve; action, closes and protrudes lips. |
| triangularis | Latin word meaning triangular; a term used in anatomy. |
| corrugator supercilii | origin, medial end of superciliary arch; insertion, skin of eyebrow; innervation, facial nerve; action, draws eyebrow downward and and toward the middle of the face. |
| nasalis | origin, maxilla; insertion,ALAR PART—ala nasi, TRANSVERSE PART—by aponeurotic expansion with fellow of opposite side; innervation, facial nerve; action,ALAR PART—aids in widening nostril, TRANSVERSE PART—pushes down cartilage of nose. |
| levator labii Superioris | levator muscle of upper lip: origin, lower orbital margin; insertion, muscle of upper lip; innervation, facial nerve; action, raises upper lip. |
| greater zygomatic - Zygomaticus Major | greater zygomatic muscle: origin, zygomatic bone in front of temporal process; insertion, corner of mouth; innervation, facia nervel; action, draws corner of mouth backward and upward. |
| masseter | origin,SUPERFICIAL PART—zygomatic process of maxilla and inferior border of zygomatic arch, DEEP PART—inferior border and medial surface of zygomatic arch; insertion,SUPERFICIAL PART—angle and ramus of mandible, DEEP PART—superior half of ramus and lateral surface of coronoid process of mandible; innervation, masseteric nerve, from mandibular division of trigeminal nerve; action, raises mandible, closes jaws |
| platysma | a subcutaneous neck muscle extending from the neck to the clavicle, acting to wrinkle the skin of the neck and to depress the jaw |
| Cant be seen on Diagram | |
| depressor angull oris | depressor muscle of angle of mouth: origin, lower border of mandible; insertion, corner (angle) of mouth; innervation, facial nerve; action, pulls down corner of mouth. |
| depressor labii inferioris | depressor muscle of lower lip: origin, anterior portion of lower border of mandible; insertion, orbicularis oris muscle and skin of lower lip; innervation, facial nerve; action, depresses (pushes down) lower lip |
| lateral pterygoid | origin,SUPERIOR HEAD—infratemporal surface of greater wing of sphenoid and infratemporal crest; INFERIOR HEAD—lateral surface of lateral pterygoid plate; insertion, neck of condyle of mandible, temporomandibular joint capsule; innervation, mandibular nerve; action, protrudes mandible, opens jaws, moves mandible from side to side. |
| medial pterygoid | origin, medial surface of lateral pterygoid plate, tuberosity of maxilla; insertion, medial surface of ramus and angle of mandible; innervation, mandibular nerve; action, closes jaws. |
| mentalis | origin, incisive fossa of mandible; insertion, skin of chin; innervation, facial nerve; action, wrinkles skin of chin |
| occipitalis | the base of the skull (called the foramen occipitalis) |
| risorius | origin, fascia over masseter muscle; insertion, skin at corner of mouth; innervation, buccal branch of facial nerve; action, pulls corner of mouth laterally. |
| Splenius Capitis | origin, lower half of nuchal ligament, spinous processes of seventh cervical and three or four upper thoracic vertebrae; insertion, mastoid part of temporal bone, occipital bone; innervation, middle and lower cervical nerves; action, extends, rotates head. |
| NECK | |
| Trapezius | origin, occipital bone, nuchal ligament, spinous processes of seventh cervical and all thoracic vertebrae; insertion, clavicle, acromion, spine of scapula; innervation, accessory nerve and cervical plexus; action, elevates shoulder, rotates scapula to raise shoulder in abduction of arm, draws scapula backward |
| sternocleidomastoid | (2 heads): origin,STERNAL HEAD—manubrium sterni, CLAVICULAR HEAD—superior surface of medial third of clavicle; insertion, mastoid process and superior nuchal line of occipital bone; innervation, accessory nerve and cervical plexus; action, flexes vertebral column, rotates head upward and to opposite side. |
| digastric | origin,ANTERIOR BELLY—digastric fossa on lower border of mandible near symphysis, POSTERIOR BELLY—mastoid notch of temporal bone; insertion, intermediate tendon on hyoid bone; innervation,ANTERIOR BELLY—mylohyoid nerve, POSTERIOR BELLY—digastric branch of facial nerve; action, raises hyoid bone, lowers jaw. |
| hyoglossus | hyoglossal muscle: origin, body and greater horn of hyoid bone; insertion, side of tongue; innervation, hypoglossal nerve; action, pushes down and pulls in tongue. |
| omohyoid | origin, superior border of scapula; insertion, lateral border of hyoid bone; innervation, upper cervical nerve through ansa cervicalis; action, depresses hyoid bone. It consists of two bellies (superior and inferior) connected by a central tendon that is attached to the clavicle by a fibrous expansion of the cervical fascia |
| sternohyoid | origin, manubrium sterni, posterior sternoclavicular ligament, clavicle; insertion, body of hyoid bone; innervation, upper ansa cervicalis; action, depresses hyoid bone and larynx |
 Internet Resources for Rhabdomyosarcoma
Internet Resources for Rhabdomyosarcoma