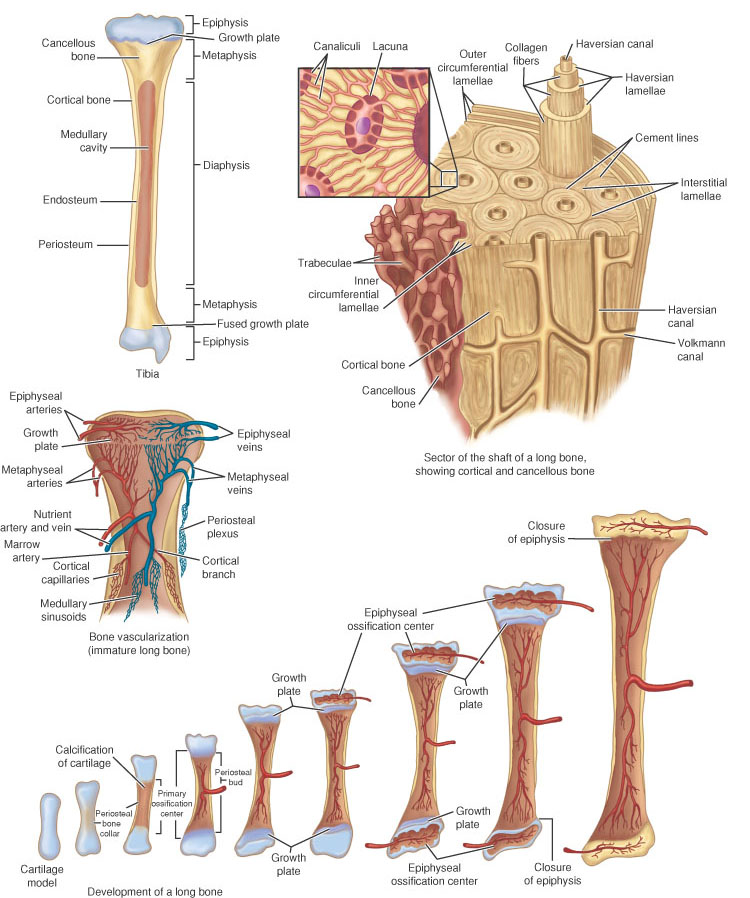
FRACTURES
| articular | joint surface |
| apophyseal | fragments torn from bone |
| avulsion | tearing or pulling of a ligament |
| blow-out | of orbital floor |
| boxer | metacarpal neck |
| bucket-handle | tear in cartilage - loop in intercondylar notch |
| burst-axial compression | vertebra - usually spinal injury |
| butterfly | looks like butterfly - comminuted fracture - 2 fragments on both sides main fracture |
| buttonhole-perforating | perforated by a missle |
| chisel | head of radius - piece detaches |
| cleavage | shelling off cartilage by small fragments |
| closed | no open wound in skin |
| Colles | displaces fragments - low end of radius |
| comminuted | splintered or crushed |
| complete | entirely broken |
| complicated | injury adjacent to bones |
| compound | open fractures |
| compression | resulting from compression |
| condylar | humerus - small fragments and condyle seperated from bone |
| dislocation | near joint displacement |
| greenstick hickorystick | one side broken other side bent |
| hangman's | axis c2 through |
| impacted | one fragment forced through another |
| indirect | distant point of injury |
| insufficiency | bone is of decreased deficiency |
| intra-articular | within a joint |
| intracapsular | within capsule of a joint |
| intrauterine | fetal bone in utero |
| Le Fort | I,II,III - maxilla |
| linear | along length |
| longitudinal | lengthwise direction |
| oblique | slanted or inclined direction |
| open | external wound - bone protrudes through skin |
| simple | closed |
| spiral fracture-torsion | bone twisted apart |
| torsion-spiral fracture | bone twisted apart |
| spontaneous | result from longstanding non-traumatic disease |
| stress | distant point of injury |
| subcapital | just below head of the bone |
| torus | localized expansion of cortex - little or no displacement to lower end of bone |
| transverse | occurs @ right angle to axis of bone |
| tuft | distal phalanx - splintered fracture |
NON-FRACTURES
| scheuermann disease | affects bone formation of vertebra |
| scoliosis | sideways curvature of spine |
| achondroplasia | cartilage and bone formation - hereditary disorder |
| ankylosing spondylitis | rheumatoid arthritis of spine |
| arthritis | inflammation of joints |
| inflammation | inflammation of joints |
| rheumatoid | most common arthritis |
| chondrosarcoma | malignant tumor of cartilage |
| degenerative joint disease | deterioration of articular cartilage |
| Ewing tumor | malignant tumor on the shaft of bone |
| sarcoma | malignant tumor |
| gout | disease deposition of urate crystals |
| Hurler syndrome | irregular formation of bone - overproduction of mucopolysaccharides (enlarged organs) |
| mucopolysaccharides | enlarged organs |
| hypophosphatasia | deficiency alkaline phosphatase |
| alkaline phosphatase | alkaline metal, sodium or potassium |
| Legg-Calve-Perthes disease | loss blood supply in head of femur |
| marfan syndrome | abnormal formation of connective tissue |
| multiple myeloma | most common bone neoplasm - tumor derived from blood cells |
| Osgood-Schlatter disease | affects tibial tubercle - where patella tibia connect |
| osteochondritis dissecans | involving joints |
| osteochondrosis | adolescence developmental disorder affecting center bone formation |
| osteogenisis imperfecta | abnormal formation of connective tissue |
| osteoid, osteoma | benign lesion |
| osteomalacia | softening of bone |
| osteomyelitis | fungal bacteria infection of bone |
| Staphylococcus aureus | bacterial infection of bone |
| osteoporosis | occurs with adequate bone density |
| kyphosis | forward hunching of the spine |
| Paget disease | degenerative disorder of bone - softening and swelling of bone |
| psoriatic arthritis | chronic skin disease |
| Reiter syndrome | nonbacterial urethritis lesions |
| rickets | overgrowth poorly mineralized bones and enlarged marrow cavities in infants |
BONES
|
|
 |
|
| accessory bone,
an occasionally occurring bone or ossicle adjoining one of the bones
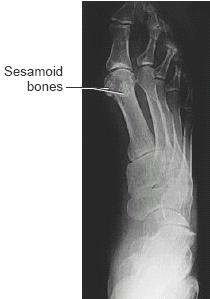
of the carpus or of the tarsus; recognized in the radiograph. acetabular bone, acetabulum. acromial bone, acromion. alar bone, os sphenoidale. Albers-Schönberg marble bones, osteopetrosis. Albrecht bone, basiotic b. alisphenoid bone, ala major ossis sphenoidalis. alveolar bone, the thin layer of bone making up the bony processes of the maxilla and mandible, and surrounding and containing the teeth; it is pierced by many small openings through which blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerve fibers pass. See also alveolar process. ankle bone, talus. astragaloid bone, talus. astragaloscaphoid bone, Pirie b. back bone, columna vertebralis. basal bone, the relatively fixed and unchangeable framework of the mandible and maxilla, which limits the extent to which teeth can be moved in the alveolar or supporting bone if the occlusion is to remain stable. basihyal bone, corpus ossis hyoidei. basilar bone, basioccipital bone, a bone developing from a separate ossification center in the fetus, which becomes the basilar part of the occipital bone. basiotic bone, a small bone of the fetus between the basisphenoid and the basioccipital bones; called also Albrecht b. basisphenoid bone, a bone in the floor of the cranium of the human embryo and many animal species. In humans, before birth it becomes part of the postsphenoidal part of the sphenoid bone (see under part); in most animals it persists as a separate bone between the basioccipital bone and the presphenoidal bone. Bertin bone, concha sphenoidalis. breast bone, sternum. bregmatic bone, os parietale. brittle bones, osteogenesis imperfecta. bundle bone, one of the two types of bones composing the alveolar bone, so called because of the continuation into it of the principal fibers of the periodontal ligament. Large amounts of more calcified cementing substance render bundle bone more resistant to x-rays than surrounding bones; therefore it appears on dental radiographs as a thin radiopaque line (hence the synonym lamina dura). Called also lamellated b. calcaneal bone, calcaneus. calf bone, fibula. cancellated bone, cancellous bone, substantia spongiosa ossium. cannon bone, a bone in the limb of hoofed animals, extending from the fetlock to the hock joint in the hind leg or the fetlock to the carpus in the foreleg; equivalent to a metacarpal or metatarsal in humans. capitate bone, os capitatum. carpal bones, ossa carpi; see under os. carpal bone, central, os centrale. carpal bone, first, os trapezium. carpal bone, fourth, os hamatum. carpal bone, great, os capitatum. carpal bone, intermediate, os lunatum. carpal bone, radial, os scaphoideum. carpal bone, second, os trapezoideum. carpal bone, third, os capitatum. carpal bone, ulnar, os triquetrum. cartilage bone, any bone that develops within cartilage, in contrast to membrane bone, ossification taking place within a cartilage model; called also endochondral b., replacement b., and substitution b. cavalry bone, rider's b. central bone, os centrale. chalky bones, osteopetrosis. cheek bone, os zygomaticum. chevron bone, the V-shaped hemal arches of the third, fourth, and fifth coccygeal vertebrae of a dog. coccygeal bone, os coccygis. coffin bone, the third or distal phalanx of the foot of a horse; called also pedal b. and os pedis. collar bone, clavicula. compact bone, substantia compacta ossium. coronary bone, small pastern bone; see pastern b. cortical bone, the compact bone of the shaft of a bone that surrounds the medullary cavity. costal bone, os costale. cranial bones, bones of cranium, ossa cranii. cribriform bone, os ethmoidale. cuboid bone, os cuboideum. cuneiform bone, external, os cuneiforme laterale. cuneiform bone, first, os cuneiforme mediale. cuneiform bone, intermediate, os cuneiforme intermedium. cuneiform bone, internal, os cuneiforme mediale. cuneiform bone, lateral, os cuneiforme laterale. cuneiform bone, medial, os cuneiforme mediale. cuneiform bone, middle, cuneiform bone, second, os cuneiforme intermedium. cuneiform bone, third, os cuneiforme laterale. cuneiform bone of carpus, os triquetrum. dermal bone, a bone developed by ossification in the skin. bones of digits of foot, ossa digitorum pedis. bones of digits of hand, ossa digitorum manus. ear bones, ossicula auditus. ectethmoid bone, labyrinthus ethmoidalis. ectocuneiform bone, os cuneiforme laterale. endochondral bone, cartilage b. entocuneiform bone, os cuneiforme mediale. epactal bone, os suturale. epactal bone, proper, os interparietale. ethmoid bone, os ethmoidale. exercise bone, a bone developed in a muscle, tendon, or fascia, as a result of excessive exercise. exoccipital bone, one of the two lateral portions of the occipital bone, developing, from separate centers of ossification, into the portions that bear the condyles. bones of face, facial bones, the bones that constitute the facial part of the skull, including the hyoid, palatine, and zygomatic bones, the mandible, and the maxilla; many authorities also include the lacrimal and nasal bones, the inferior nasal concha, and the vomer, and exclude the hyoid bone. Called also ossa faciei and ossa facialia. femoral bone, femur (def. 1). fibular bone, fibula. bones of fingers, ossa digitorum manus. flank bone, os ilium. flat bone, os planum. frontal bone, os frontale. funny bone, the region of the median condyle of the humerus where it is crossed by the ulnar nerve. hamate bone, os hamatum. haunch bone, os coxae. heel bone, calcaneus. hip bone, os coxae. humeral bone, humerus. hyoid bone, os hyoideum. iliac bone, os ilium. incarial bone, os interparietale. incisive bone, os incisivum. innominate bone, os coxae. intermediate bone, os lunatum. interparietal bone, os interparietale. intrachondrial bone, osseous tissue occurring in cartilage matrix which has undergone calcification; found particularly in patches within the middle layer of the otic capsule. Called also globuli ossei. irregular bone, os irregulare. ischial bone, os ischii. ivory bones, osteopetrosis. jaw bone, lower, mandibula. jaw bone, upper, maxilla. jugal bone, os zygomaticum. lacrimal bone, os lacrimale. lacrimal bone, lesser, the lacrimal hamulus when it exists as a part separated from the rest of the lacrimal bone. lamellar bone, the normal type of adult bone, organized in layers (lamellae), which may be parallel (cancellous bone) or concentrically arranged (compact bone). lamellated bone, one of the two types of bone composing the alveolar bone, with some lamellae roughly parallel with the marrow spaces and others forming haversian systems. Cf. bundle b. lenticular bone of hand, lentiform bone, os pisiforme. lingual bone, os hyoideum. long bone, os longum. lunate bone, os lunatum. malar bone, os zygomaticum. marble bones, osteopetrosis. mastoid bone, processus mastoideus ossis temporalis. maxillary bone, maxilla. maxilloturbinal bone, concha nasalis inferior. membrane bone, any bone that develops within a connective tissue membrane, in contrast to cartilage bone. mesethmoid bone, a cranial bone present in some vertebrates, forming the most anterior part of the internal base of the cranium. mesocuneiform bone, os cuneiforme intermedium. metacarpal bones, ossa metacarpi. metacarpal bone, middle, metacarpal bone, third, os metacarpi tertium. metatarsal bones, ossa metatarsi. multangular bone, accessory, os centrale. multangular bone, larger, os trapezium. multangular bone, smaller, os trapezoideum. nasal bone, os nasale. navicular bone of foot, os naviculare. navicular bone of hand, os scaphoideum. nonlamellated bone, woven b. occipital bone, os occipitale. odontoid bone, dens axis. orbitosphenoidal bone, ala minor ossis sphenoidalis. palate bone, palatine bone, os palatinum. parietal bone, os parietale. pastern bone, either of two bones of the horse's foot just proximal to the hoof: the large pastern bone is the first phalanx and the small pastern bone (called also coronary b.) is the second phalanx. pedal bone, coffin b. pelvic bone, os coxae. periosteal bone, bone that is developed directly from and beneath the periosteum. petrosal bone, petrous bone, pars petrosa ossis temporalis. phalangeal bones of foot, ossa digitorum pedis. phalangeal bones of hand, ossa digitorum manus. Pirie bone, an occasionally occurring ossicle found above the head of the talus; called also astragaloscaphoid b. pisiform bone, os pisiforme. plowshare bone, pygostyle. pneumatic bone, os pneumaticum. postsphenoid bone, postsphenoidal bone, see under part. postulnar bone, os pisiforme. prefrontal bone, pars nasalis ossis frontalis. preinterparietal bone, a wormian bone sometimes observed, detached from the anterior part of the interparietal bone. premaxillary bone, premaxilla. presphenoid bone, presphenoidal bone, see under part. primitive bone, woven b. pterygoid bone, processus pterygoideus ossis sphenoidalis. pubic bone, os pubis. pyramidal bone, os triquetrum. radial bone, radius (def. 2). replacement bone, cartilage b. resurrection bone, os sacrum. rider's bone, a localized ossification of the inner aspect of the lower end of the tendon of the adductor muscle of the thigh (adductor tubercle), sometimes seen in horseback riders; called also cavalry b. Riolan bones, small bones resembling wormian (sutural) bones, sometimes found in the suture between the occipital bone and the petrous portion of the temporal bone. rostral bone, a bone supporting the apex of the nose in cattle or of the snout in pigs. rudimentary bone, a bone that has only partially developed. sacral bone, os sacrum. scaphoid bone, os scaphoideum. scaphoid bone of foot, os naviculare. scaphoid bone of hand, os scaphoideum. scapular bone, scapula. semilunar bone, os lunatum. sesamoid bones, numerous ovoid nodular bones, often small, usually found embedded within a tendon or joint capsule, principally in the hands and feet (ossa sesamoidea manus and ossa sesamoidea pedis, respectively); two sesamoid bones, the fabella and patella, are associated with the knee. sesamoid
bones of foot,
ossa sesamoidea
pedis. |
SKELETON - the hard framework of the animal body, especially the bony framework of the body of higher vertebrate animals; the bones of the body collectively. See Plate 45. See also endoskeleton, exoskeleton, and visceral skeleton.
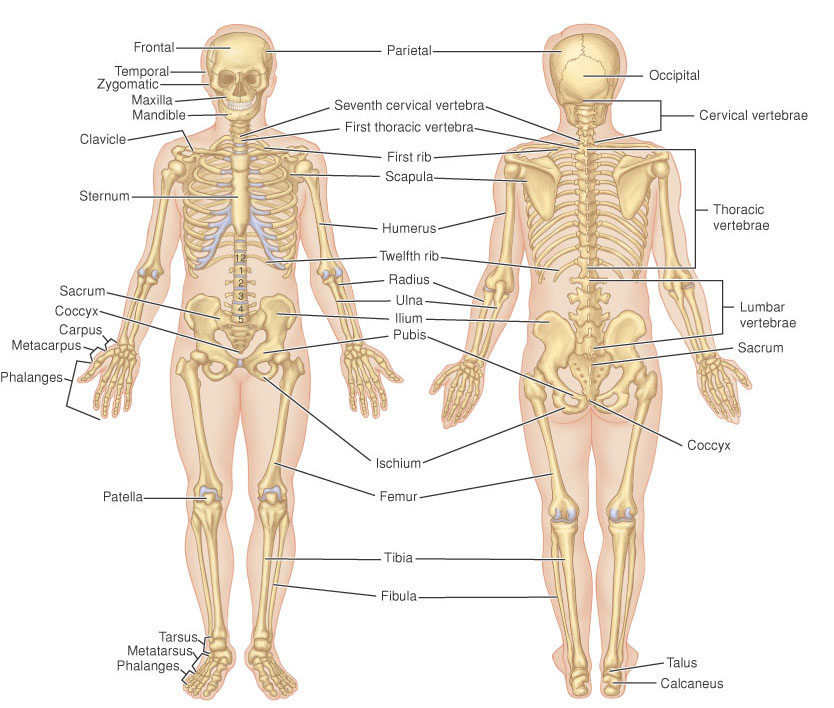
appendicular skeleton, skeleton appendicula´re,
the bones of the upper and lower limbs.
axial skeleton, skeleton axia´le, the bones of the cranium, vertebral
column, ribs, and sternum.
cardiac skeleton, the fibrous or fibrocartilaginous framework that
supports and gives attachment to the cardiac muscle fibers and valves, and the
roots of the aorta and pulmonary trunk; it includes the anuli fibrosi cordis,
left and right fibrous trigones, membranous part of the interventricular septum,
and the infundibular tendon. Called also
fibrous s. of heart.
fibrous skeleton of heart,
cardiac s.
skeleton of heart,
cardiac s.
skeleton mem´bri inferio´ris li´beri,
pars libera membri
inferioris.
skeleton mem´bri superio´ris li´beri,
pars libera membri
superioris.
thoracic skeleton, skeleton thora´cicus,
s. thoracis.
skeleton thora´cis, skeleton of thorax: the skeletal framework enclosing
the thorax, consisting of the thoracic vertebrae and intervertebral disks, the
ribs and costal cartilages, and the sternum; called also
rib cage and
thoracic cage.
visceral skeleton, the portion of the skeleton that protects the viscera,
including the sternum, ribs, pelvis, and os coxae.