|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Consistency is not readily evaluated by simply looking at a specimen. That's right. You actually have to touch those specimens in the pan. It's really not that bad - you'll get used to it. Besides, that's what gloves are for.However, you still need to know some handy words to use to describe those organs. "Squishy" and "slimy" just don't cut it. You can't say that coagulating blood looks "like gravy" either. Learn the word "viscous" and use it instead.
So why are these adjectives so terrible? Why? Because they are one or more of the following:
- vague or redundant (e.g. pale, yellowish in color)
- open to interpretation (e.g. melon)
- describe food (e.g. wine-colored, honey-colored)
- excessively verbose (e.g. scarlet instead of red)
Words you should use
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The ability to estimate the size of lesions accurately is an important skill in pathology. Often people lack a good sense of small sizes in the metric system. Students may be comfortable with "guesstimating" the length of a mass to be, say, two inches, but when asked how many centimeters that is they will often guess seven or eight when really it is closer to five centimeters.
To eliminate this "guesstimating" problem, it is best to pick a readily accessible (and socially acceptable) part of your body such as the length of a phalanx of your index finger or the width of your thumb. Measure this part of your body with a metric ruler.
The example at right is to scale. The ruler in the photo is actually 3 cm long, so you can hold up your finger to the screen now and measure the approximate length of part of your finger.
Memorize this number and then whenever you need to measure a lesion, you can simply pull out your handy-dandy finger and use your pre-measured digit as a mini-ruler.
A few examples are presented in this section for you, but you will get more practice in the "Practice Questions" section.
| Similarly, you can measure the thickness of your index finger. The finger at left is about 1.5 cm wide. |

|
So here's a test for you. We'll start with a
fairly easy one. An object you see just about every day. |
| That's right. A quarter. SO. How wide would you say this quarter is? (You can cheat and compare it to the pink ruler in the other
picture if you really need to...). |
I think you've got it! So now here is a lesion for you to try your hand at (pardon the pun).
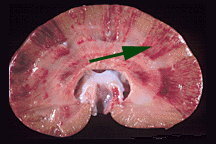
(Assume kidney shown actual size.)
How wide would you say the wedge-shaped infarct indicated by the arrow is at the middle?
A. 4.00 cm
B. 2.50 cm
C. 0.50 in
D. 1.00 cm
E. 0.50 cm
Once pathologists have finished describing lesions, they must interpret what they have found and develop a morphologic diagnosis. A morphologic diagnosis is a short phrase that sums up the important aspects of the lesion and is a way to communicate these aspects to other medical professionals in a precise way.The components of a morphologic diagnosis are:
These four are the basics, but sometimes other modifiers can be used to refer to Distribution (abbreviated as: d)
- Severity (abbreviated as: s)
- Time (abbreviated as: t)
- Lesion (abbreviated as: l)
- Anatomic site (abbreviated as: a)
For example, if you saw a swollen, dark red spleen that dripped blood when you cut it, the morphologic diagnosis would be:
Severe, acute, diffuse, splenic congestion. s t d a l
Similarly, if you saw a kidney with a small wedge-shaped area in the parenchyma that was firm and white/tan and shrunken below the level of the rest of the normal surface, your morphologic diagnosis would be:
Mild, chronic, focal, renal infarct s t d a l
Morphologic diagnosis is very, very important (hint-hint). It is the interpretation of the abnormalities which you have just assessed and described.Some morphologic diagnoses, however, do not have all five components because they do not really fit biologically. For example, neoplasms cannot really be "timed" or graded as to severity. So a morphologic diagnosis of a neoplasm would simply be:
It may seem tough now, but don't worry - you will get a chance to review these concepts and try your hand at coming up with morphologic diagnoses in the "Practice Questions" section.
Hepatic carcinoma a l
![]()
- A-, an- (prefix)
- without.
e.g. aplasia - without or lack of formation.
- Abscess
- a localized collection of pus in a cavity formed by the disintegration of tissue.
- Acrodermatitis
- inflammation of the skin of the extremities, particularly of the paws or feet.
e.g. lethal acrodermatitis - an inherited autosomal recessive disease in bull terriers relating to zinc metabolism.
- Adeno- (prefix)
- gland.
e.g. adenitis - inflammation of a gland.
- Adenocarcinoma
- a malignant tumor of epithelial cells arranged in glandular patterns.
- Adenoma
- a benign epithelial tumor in which the cells form glandular structures or are derived from glandular epithelium.
- Agenesis
- absence, failure of formation or imperfect development of any part.
- Amelanotic
- in reference to a melanoma, amelanotic refers to a melanoma that contains little or no pigment.
- Anis-, aniso- (prefix)
- unequal; dissimilar.
e.g. anisokaryosis - inequality in the size of the nuclei of cells.
(.wav, 50 K)
(.aiff, 33K)
- -angio (suffix)
- vessel.
e.g. lymphangitis - inflammation of a lymph vessel.
- Ante- (prefix)
- before in time or space.
e.g. ante mortem - before death.
- Anti- (prefix)
- against; counteracting.
e.g. antitoxin - an antibody to a toxin.
- Aplasia
- Defective development or congenital absence of an organ or tissue.
- Arthr(o)- (prefix)
- joint; articulation.
e.g. arthrolith - a calculous deposit within a joint.
- Atresia (adj. atretic)
- closed; absence of a normal opening or normally patent lumen
- Atrophy
- a wasting of tissues, organs or the entire body; caused by death and resorption of cells, diminished cellular proliferation, pressure, ischemia, malnutrition, decreased function or hormonal changes.
- Auto- (prefix)
- self.
e.g. autolysis - self-dissolution; the post-mortem enzymatic degradation of cells.
(.wav, 28K)
(.aiff, 17K)
- Axilla
- the armpit.
- Bilateral
- affecting both sides.
- Boss
- a round eminence as found at the base of a horn.
- Bosselated
- marked or covered with round eminences (bosses) resembling those found at the base of a horn.
- Botryoid
- shaped like a bunch of grapes.
(.wav, 40K)
(.aiff, 33K)
- Bovine Malignant Catarrhal Fever
- malignant catarrhal fever is an acute, highly fatal, viral, infectious disease of cattle and sheep , characterized by an erosive stomatitis, gastroenteritis and erosions of the mucosa of the upper respiratory tract.
(.wav, 41K)
(.aiff, 33K)
- Cancer
- a group of neoplastic diseases in which there is a transformation of normal cells into malignant cells. The cells proliferate in an abnormal way resulting in a malignant, cellular tumor. See also Metastatic.
- Caseous
- having a consistency like that of cottage cheese.
- Catarrh
- inflammation of a mucous membrane with free discharge.
(.wav, 20K)
(.aiff, 17K)
- -cele (suffix)
- tumor; herniation.
e.g. meningocoele - hernial protrusion of meninges.
- Cellulitis
- a diffuse inflammatory process within solid tissues characterized by edema, redness, pain and interference with function. Cellulitis often occurs in the loose tissues beneath the skin, but may also occur in mucous membranes and in muscle bundles surounding organs.
- -centesis (suffix)
- puncture.
e.g. thoracentesis - puncture of the pleural cavity.
- Chol- (prefix)
- bile.
e.g. cholelith - gallstone; bile stone.
- Congenital
- exsisting at birth.
referring to certain mental or physical traits or peculiarities, malformations, diseases, which may be either hereditary or due to some influence occuring during gestation even up to the moment of birth. See also Hereditary.
- Contralateral
- affecting or pertaining to the opposite side.
- Corrugated
- having a ripple-like distortion.
- Cyanosis
- a bluish discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes due to an excessive concentration of reduced (deoxygenated) hemoglobin in the blood.
- Cyst
- an abnormal sac filled with gas, fluid, or semi-solid material that is lined by a membrane.
- Cyst(o)- (prefix)
- bladder.
e.g. cystitis - inflammation of the urinary bladder.
- Cyt(o)- (prefix)
- cell.
e.g. cytomegaly - marked enlargement of cells.
- Derma-, dermat(o)- (prefix)
- skin.
e.g. dermatitis - inflammation of the skin.
- Dia- (prefix)
- through; between; ss.
e.g. diarrhea - fecal matter flowing through the bowel.
- Diffuse
- not definitely localized or limited; spread widely through a tissue or substance.
- Diphtheritic membrane
- a thin coating on the surface of an epithelial lined organ (e.g. intestine) that is composed of necrotic cellular debris, inflammatory cells and fibrin.
- Dys- (prefix)
- difficult; bad; abnormal.
e.g. dysplasia - abnormal formation.
e.g. dyspnea - shortness of breath; difficulty breathing.
- Dysgenesis
- defective embryonic development.
- Dysplasia
- abnormal tissue development.
- Dystopia
- displacement. See also Malposition.
- -ectasis (suffix)
- to stretch; dilate.
e.g. bronchiectasis - dilatation of bronchi. The noun form is ectasia
- -ectomy (suffix)
- excision.
e.g. cholecystectomy - excision of the gallbladder.
(.wav, 39K)
(.aiff, 33K)
- Ecchymosis
- A purplish patch caused by extravasation of blood into the tissues differing from petechiae only in size. See also Petechia and Purpura.
(.wav, 34K)
(.aiff, 33K)
- Edema
- an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the cavities and intercellular spaces of the body.
- Em-, en-, in- (prefix)
- into.
e.g. encyst - to enclose in a cyst or sac.
- Embolus
- a clot, usually part or all of a thrombus, carried by a larger vessel and forced into a smaller vessel, thus obstructing blood flow. See also Embolism and Thromboembolism.
- Embolism
- the sudden blocking of an artery by a clot of material (embolus). The process of the formation of an embolus.
- -emesis (suffix)
- vomit.
e.g. hematemesis - vomiting blood.
(.wav, 33K)
(.aiff, 33K)
- -emia (suffix)
- blood.
e.g. lipidemia - excess lipid in the blood.
- Endo- (prefix)
- within.
e.g. endocardium - the inner lining of the heart.
e.g. endometrium - the mucous membrane lining of the uterus.
- Enter(o)- (prefix)
- intestine.
e.g. enteritis - inflammation of the intestine.
- Epi- (prefix)
- upon; over.
e.g. epibulbar - situated upon the eyeball.
- Epicardium
- the inner layer of the serous pericardium which is in contact with the heart.
- Eroded
- having a shallow or superficial ulceration.
- Etiology
- the causative agent in a lesion.
(.wav, 31K)
(.aiff, 17K)
- Ex(o)- (prefix)
- out of; away from; outside of.
e.g. exophytic - projecting out from a surface.
- Fibrin
- a filamentous protein formed from the precursor fibrinogen by the enzyme thrombin.
- Fistula
- an abnormal, tube-like passage from a hollow organ to the surface, or from one organ to another.
e.g. esophageal fistula - a communication between the esophagus and some portion of the respiratory tract.
(.wav, 23K)
(.aiff, 17K)
- Flocculent
- having downy or flaky shreds.
(.wav, 27K)
(.aiff, 17K)
- Friable
- breaks apart or crumbles easily.
(.wav, 29K)
(.aiff, 17K)
- Gastroenteritis
- inflammation of the lining of the stomach and intestine.
- -genesis(suffix)
- origin.
e.g. spermatogenesis - formation of sperm.
- Granuloma
- a focal collection of activated macrophages.
(.wav, 40K)
(.aiff, 33K)
- Granulomatous
- composed of granulomas.
(.wav, 46K)
(.aiff, 33K)
- Grey matter
- the grey nervous tissue of the brain and spinal cord consisting of the cell bodies and dendrites of nerve cells rather than the myelinated axons.
- Grumose
- lumpy or clotted.
(.wav, 24K)
(.aiff, 17K)
- Hema-, hemato, haemo- (british)- (prefix)
- blood
e.g. hematocrit - the volume percentage of erythrocytes in whole blood.
- Hemangio- (prefix)
- blood vessel.
e.g. hemangiosarcoma - malignant tumor of a blood vessel.
- Hematoma
- a localized collection of extravasated blood, usually clotted.
- Hereditary
- transmitted from parent to offspring; derived from ancestry. See also Congenital.
- Hetero- (prefix)
- dissimilar.
e.g. heterocellular - composed of more than one type of cell.
- Histiocyte
- a large, phagocytic cell of the reticuloendothelial system; a macrophage.
- Histiocytoma
- a common neoplasm of young dogs composed of round histiocytic cells, thought to be Langerhan's cells. Most tumors spontaneously regress.
- Homeo-, homo- (prefix)
- similar; same.
e.g. homeotypical - resembling the normal or usual type.
- Hydro-, hygro- (prefix)
- water; fluid.
e.g. hydronephrosis - distension of the renal pelvis and calices with urine.
Hydroureter- distension of the ureter with fluid due to obstruction. Hydroureter is often accompanied by hydronephrosis if the obstruction is in the bladder trigone or more distal.
- Hyper- (prefix)
- above and beyond; excessive.
e.g. hyperacidity - excessive acidity.
e.g. hyperchromasia - excessive pigmentation
- Hyperemia
- presence of an increased amount of blood in a part or an organ.
- Hypertrophy
- an increase in the size of a cell, tissue or organ usually as a physiologic response to a stimulus.
(.wav, 40K)
(.aiff, 33K)
- Hypoplasia
- underdevelopment of a tissue or organ usually due to a decrease in the number of cells.
- Hypotonia
- abnormally decreased tonicity, tension or strength; ocular hypotony refers to low intraocular pressure.
(.wav, 26K)
(.aiff, 17K)
- -iasis (suffix)
- a process, especially a morbid one.
e.g. amebiasis - the state of being infected with amebae.
- Idiopathic
- occurring without known cause.
- Imperforate
- atretic; closed.
(.wav, 35K)
(.aiff, 33K)
- Indurated
- abnormally hard.
- Infarct
- a localized area of ischemic necrosis produced by the occlusion of the blood vessels - either arterial supply or venous drainage.
- Infra- (prefix)
- beneath.
e.g. infraorbital - beneath the eye.
- Inter- (prefix)
- between.
e.g. intercellular - between two cells.
- Intra- (prefix)
- within.
e.g. intracellular - within cells.
- Ipsilateral
- affecting or pertaining to the same side.
- Ischemia
- a local deficiency of blood due in part to functional constriction or actual mechanical obstruction of a blood vessel.
(.wav, 29K)
(.aiff, 17K)
- -itis (suffix)
- inflammation.
e.g. appendicitis - inflammation of the appendix.
- Johne's Disease
- an infection of cattle, sheep and goats cause by Mycobacterium paratuberculosis characterized by diarrhea and thickening and corrugation of the intestinal wall.
(.wav, 34K)
(.aiff, 33K)
- Leio- (prefix)
- smooth.
e.g. leiomyoma - a benign tumor of smooth muscle cells.
(.wav, 35K)
(.aiff, 33K)
- Lesion
- an alteration or abnormality in a tissue or cell; a pathological change.
- Leuc-, leuk- (prefix)
- white.
e.g. leukocyte - a white blood cell.
e.g. leukopenia - reduction in the number of leukocytes in the blood.
- Leukoencephalitis
- inflammation of the white matter of the brain.
- Lip(o)- (prefix)
- fat; lipid.
e.g. lipoma - a benign tumor of fat cells.
- Lith- (prefix)
- stone.
e.g. lithotomy - removal of a stone.
- Lymphangiectasia
- dilation of the lymphatic vessels; may be congenital or acquired.
(.wav, 73K)
(.aiff, 33K)
- Lymphoma
- a neoplastic disorder of lymphocytes.
- -lysis (suffix)
- to dissolve.
e.g. autolysis - self-dissolution.
- -malacia (suffix)
- softening.
e.g. osteomalacia - softening of the bone.
- Macro- (prefix)
- large.
e.g. macrophage - a large, mononuclear, phagocytic blood cell.
- Malignant
- having the properties of anaplasia, invasiveness and metastasis; Tending to become progressively worse and to result in death. See also Cancer.
- Malposition
- faulty or abnormal position of a part of the body. See also Dystopia.
- Mega- (prefix)
- great.
e.g. megakaryocyte - the giant cell of the bone marrow that has a greatly lobulated nucleus and gives rise to blood platelets.
- -megaly (suffix)
- great, large.
e.g. splenomegaly - enlargement of the spleen.
- Melan- (prefix)
- black.
e.g. melanin - black pigment of the hair, skin, ciliary body, choroid, retina, and certain nerve cells.
- Meninges
- the three membranes covering the brain and spinal cord - the dura mater, arachnoid, and pia mater.
- Meningo- (prefix)
- membrane; meninges.
e.g. meningoencephalitis - inflammation of the brain and its meninges.
- Mesothelium
- the layer of flat cells lining the body cavity of the embryo; in the adult, it forms the simple squamous epithelium that covers the true serous membranes of the body. Mesothelium is derived from mesoderm.
- Metastatic
- a tumor that has transfered from one organ (or part) to another not directly connected to it. See also Cancer.
(.wav, 35K)
(.aiff, 33K)
- Micro- (prefix)
- small.
e.g. microhepatia - a small liver.
- Morphologic diagnosis
- the interpretation of the abnormalities in terms of severity, time, lesion and anatomic site. For example: severe, chronic, glomerulonephritis.
- Mucous
- (adj.) relating to or resembling mucus.
- Mucus
- (n.) the glandular, free slime of the mucous membranes.
- My-, myo- (prefix)
- muscle.
e.g. leiomyosarcoma - a malignant tumor of smooth muscle cells.
(.wav, 38K)
(.aiff, 33K)
- Myelin
- the lipid substance forming a sheath around the axons of certain nerve fibers.
- Myx- (prefix)
- mucus.
e.g. myxedema - mucinous edema (swelling).
(.wav, 27K)
(.aiff, 33K)
- Necr- (prefix)
- death.
e.g. necrosis - the morphologic changes indicative of cell death, indicated by characteristic nuclear and cytoplasmic changes.
- Necropsy
- examination of a body after death.
- Nephr- (prefix)
- kidney.
e.g. nephrectomy - surgical removal of the kidney.
- -oid (suffix)
- like, resembling.
e.g. leukemoid - like leukemia.
- Oligo- (prefix)
- few; scanty.
e.g. oligochromemia - deficiency of hemoglobin in the blood.
(.wav, 29K)
(.aiff, 17K)
- -ologous (suffix)
- relating to.
e.g. homologous - of similar structure.
- -oma (suffix)
- tumor.
e.g. osteoma - tumor of bone.
- -opathy (suffix)
- disease.
e.g. nephropathy - any disease of the kidney.
(.wav, 32K)
(.aiff, 17K)
- -orrhea (suffix)
- flow; discharge.
e.g. leukorrhea - white discharge.
- -oscopy (suffix)
- view.
e.g. endoscopy - to view the inside, specifically: the intestine.
(.wav, 32K)
(.aiff, 17K)
- -osis (suffix)
- a process, especially a morbid one.
e.g. diverticulosis - involvement with diverticula.
- Osteo- (prefix)
- bone.
e.g. osteomyelitis - inflammation of bone.
- Osteoid
- resembling bone.
- -ostomy (suffix)
- mouth.
e.g. gastrostomy - creation of an artificial gastric fistula.
- -otomy (suffix)
- cut.
e.g. cholecystotomy - incision into the gallbladder.
- Panniculitits
- a rare, multifactorial inflammatory condition involving subcutaneous fat.
- Panniculus
- a layer of membrane.
- Papillary
- having small nipple-shaped projections.
- Papilloma
- the common wart; a benign tumor derived from epithelium. They are caused by papillomaviruses.
- Papules
- a small circumscribed, solid, elevated lesion of the skin.
- Para- (prefix)
- beside.
e.g. para-aortic - beside the aorta.
e.g. parauterine - beside the uterus.
- Parenchyma
- the essential or functional elements of an organ.
- Patent
- open, exposed or unobstructed.
e.g. patent ductus arteriosus - an abnormal persistence after birth of an open lumen in the ductus arteriosus, between the pulmonary artery and the aorta.
- Pathogenesis
- the sequence of events that leads to a disease or morbid process. It may be, for example, hormonal, chemical, infectious, genetic or traumatic in nature.
- Pathology
- the science and study of disease, especially the causes and development of abnormal conditions both gross and microscopic.
- Pedunculated
- elevated, as on a stem (peduncle).
(.wav, 50K)
(.aiff, 33K)
- -penia (suffix)
- poverty.
e.g. thrombocytopenia - decrease in blood platelets.
- Peri- (prefix)
- around.
e.g. peribronchial - around the bronchus.
- Pericardium
- the fibroserous sac enclosing the heart and the roots of the great vessels of the heart. It is composed of a fibrous external layer and a serous inner layer.
- Petechia
- a pinpoint, non-raised, purplish-red spot caused by intradermal or subcutaneous hemorrhage. Plural is petechiae.
(.wav, 25K)
(.aiff, 17K)
- Peyer's Patches
- ovoid, elevated patches of closely packed lymphoid follicles in the mucosa and submucosa of the small intestine. Also called aggregated lymphoid follicles.
- -phage (suffix)
- eat; devour.
e.g. macrophage - a cell which devours (phagocytoses).
- Phago- (prefix)
- eat; devour.
e.g. phagocyte - any cell that ingests foreign material, other cells or microorganisms.
- Pheochromocytoma
- (pheo=dusky) (chromo=color) (cyt=cell) (oma=tumor)
a small tumor of chromaffin cells, usually of the adrenal medulla, but occasionally of the chromaffin tissue of sympathetic paraganglia. Functional tumors secrete catecholamines.
(.wav, 83K)
(.aiff, 50K)
- Phleb- (prefix)
- vein.
e.g. phlebitis - inflammation of the vein.
(.wav, 26K)
(.aiff, 17K)
- Pinna
- the projecting part of the ear; also known as the auricle.
- -plasia (suffix)
- to form.
e.g. hyperplasia - an increase in the number of cells in a tissue or organ, usually as a physiologic response to a stimulus.
(.wav, 47K)
(.aiff, 17K)
- -pnea (suffix)
- breath.
e.g. dyspnea - labored or difficult breathing.
(.wav, 19K)
(.aiff, 17K)
- Polyp
- a spheroidal mass that protrudes upwards or outwards from a normal surface. Polyps may be hyperplastic, inflammatory, or neoplastic.
e.g. pedunculated polyp - a polyp attached by a thin stalk (peduncle).
e.g. sessile polyp - a polyp with a broad base (sessile).
- Polypoid
- Resembling a polyp.
- Purpura
- a hemorraghic disease characterized by extravasation of blood into the tissues producing spontaneous ecchymoses and petechiae.
(.wav, 18K)
(.aiff, 17K)
- Pus
- a protein-rich liquid inflammation product comprised of leukocytes, a thin fluid and cellular debris.
- Prognosis
- a prediction of the outcome of the pathological process or disease.
- -ptosis (suffix)
- falling.
e.g. ptosis - drooping, specifically: of the eyelid.
(.wav, 18K)
(.aiff, 17K)
- Pyo- (prefix)
- pus.
e.g. pyometra - an accumulation of pus within the uterus.
e.g. pyogranuloma - an infiltration of polymorphonuclear cells into an area of chronic inflammation characterized by mononuclear cells, macrophages, lymphocytes and even plasma cells.
- Pyelonephritis (nephropyelitis)
- inflammation of the kidney and renal pelvis often by ascending bacterial infection.
- Reniform
- shaped like a kidney.
- Resilient
- having the ability to return to an original shape after having been compressed or deformed.
- -rhage, -rrhage, -rrhagia (suffix)
- discharge.
e.g. hemorrhage - discharge of blood.
- -rrhea (suffix)
- abnormal or excessive flow.
e.g. steatorrhea - excessive lipid in the feces.
(.wav, 33K)
(.aiff, 33K)
- Saponification
- the hydrolysis of a fat by alkali with the formation of a soap and glycerol.
- Sclero- (prefix)
- hard.
e.g. scleroma - a hardened patch of skin or mucous membrane.
- Serosa
- any serous membrane.
- Serous Membrane
- the membrane lining the walls of the body cavities and enclosing the contained organs. It is a mesothelium lying upon a connective tissue layer and secretes a watery serous fluid.
- Serpiginous
- having a wavy border.
(.wav, 44K)
(.aiff, 33K)
- Serrated
- having a saw-like edge.
- Sessile
- attached by a broad base.
- -stasis (suffix)
- standing still.
e.g. hemostasis - arrest of blood circulation.
- Stea- (prefix)
- lipid.
e.g. steatorrhea - excessive lipid in the feces.
(.wav, 33K)
(.aiff, 33K)
- Stenosis
- a stricture of any canal.
- Stoma- (prefix)
- mouth.
e.g. stomatology - the study of the mouth and its diseases.
- Stomatitis
- inflammation of the mucosa of the mouth.
- Suppurative
- containing pus.
(.wav, 43K)
(.aiff, 33K)
- Syncope
- a temporary loss of consciousness due to insufficient cerebral blood flow; fainting.
- Thromboembolism
- the lesion created by a thromboembolus.
- Thromboembolus
- a clot of material that breaks free from a primary site, is transported in the bloodstream and becomes lodged and adhered at a secondary site.
- -trophy (suffix)
- nourish.
e.g. dystrophy - defective or faulty nutrition.
- Ulcerated
- having a local defect or excavation of the epithelium of an organ or tissue through the basement membrane.
- Umbilicated
- marked by depressed spots resembling the umbilicus.
- Umbilicus
- the scar marking the site of entry of the umbilical cord into the fetus. It is inconspicuous in most domestic species.
- Unilateral
- affecting only one side.
- -uria (suffix)
- urine.
e.g. proteinuria - protein in the urine.
- Verruca
- a wart.
- Verrucous
- rough; wart-like.
- Viscous
- thick, coagulated; sticky or gummy.
- White matter
- the white nervous tissue of the brain and spinal cord consisting of the conducting, myelinated fibers.
- A-, an- (prefix)
- without.
e.g. aplasia - without or lack of formation.
- Abscess
- a localized collection of pus in a cavity formed by the
disintegration of tissue.
- Acrodermatitis
- inflammation of the skin of the extremities, particularly of the
paws or feet.
e.g. lethal acrodermatitis - an inherited autosomal recessive disease in bull terriers relating to zinc metabolism.
- Adeno- (prefix)
- gland.
e.g. adenitis - inflammation of a gland.
- Adenocarcinoma
- a malignant tumor of epithelial cells arranged in glandular
patterns.
- Adenoma
- a benign epithelial tumor in which the cells form glandular
structures or are derived from glandular epithelium.
- Agenesis
- absence, failure of formation or imperfect development of any
part.
- Amelanotic
- in reference to a melanoma, amelanotic refers to a melanoma that
contains little or no pigment.
- Anis-, aniso- (prefix)
- unequal; dissimilar.
e.g. anisokaryosis - inequality in the size of the nuclei of cells.
- -angio (suffix)
- vessel.
e.g. lymphangitis - inflammation of a lymph vessel.
- Ante- (prefix)
- before in time or space.
e.g. ante mortem - before death.
- Anti- (prefix)
- against; counteracting.
e.g. antitoxin - an antibody to a toxin.
- Aplasia
- Defective development or congenital
absence of an organ or tissue.
- Arthr(o)- (prefix)
- joint; articulation.
e.g. arthrolith - a calculous deposit within a joint.
- Atresia (adj. atretic)
- closed; absence of a normal opening or normally
patent lumen
- Atrophy
- a wasting of tissues, organs or the entire body; caused by death
and resorption of cells, diminished cellular proliferation,
pressure, ischemia, malnutrition, decreased function or hormonal
changes.
- Auto- (prefix)
- self.
e.g. autolysis - self-dissolution; the post-mortem enzymatic degradation of cells.
- Axilla
- the armpit.
B
- Bilateral
- affecting both sides.
- Botryoid
- shaped like a bunch of grapes.
C
- Cancer
- a group of neoplastic diseases in which there is a
transformation of normal cells into malignant cells. The cells
proliferate in an abnormal way resulting in a malignant, cellular
tumor. See also Metastatic.
- Caseous
- having a consistency like that of cottage cheese.
- Catarrh
- inflammation of a mucous membrane with free discharge.
- -cele (suffix)
- tumor; herniation.
e.g. meningocoele - hernial protrusion of meninges.
- Cellulitis
- a diffuse inflammatory process within solid tissues
characterized by edema, redness, pain and interference with
function. Cellulitis often occurs in the loose tissues beneath the
skin, but may also occur in mucous membranes and in muscle bundles
surounding organs.
- -centesis (suffix)
- puncture.
e.g. thoracentesis - puncture of the pleural cavity.
- Chol- (prefix)
- bile.
e.g. cholelith - gallstone; bile stone.
- Congenital
- exsisting at birth.
referring to certain mental or physical traits or peculiarities, malformations, diseases, which may be either hereditary or due to some influence occuring during gestation even up to the moment of birth. See also Hereditary.
- Contralateral
- affecting or pertaining to the opposite side.
- Corrugated
- having a ripple-like distortion.
- Cyanosis
- a bluish discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes due to
an excessive concentration of reduced (deoxygenated) hemoglobin in
the blood.
- Cyst
- an abnormal sac filled with gas, fluid, or semi-solid material
that is lined by a membrane.
- Cyst(o)- (prefix)
- bladder.
e.g. cystitis - inflammation of the urinary bladder.
- Cyt(o)- (prefix)
- cell.
e.g. cytomegaly - marked enlargement of cells.
D
- Derma-, dermat(o)- (prefix)
- skin.
e.g. dermatitis - inflammation of the skin.
- Dia- (prefix)
- through; between; ss.
e.g. diarrhea - fecal matter flowing through the bowel.
- Diffuse
- not definitely localized or limited; spread widely through a
tissue or substance.
- Diphtheritic membrane
- a thin coating on the surface of an epithelial lined organ (e.g.
intestine) that is composed of necrotic cellular debris,
inflammatory cells and fibrin.
- Dys- (prefix)
- difficult; bad; abnormal.
e.g. dysplasia - abnormal formation.
e.g. dyspnea - shortness of breath; difficulty breathing.
- Dysgenesis
- defective embryonic development.
- Dysplasia
- abnormal tissue development.
- Dystopia
- displacement. See also Malposition.
E
- -ectasis (suffix)
- to stretch; dilate.
e.g. bronchiectasis - dilatation of bronchi. The noun form is ectasia
- -ectomy (suffix)
- excision.
e.g. cholecystectomy - excision of the gallbladder.
- Ecchymosis
- A purplish patch caused by extravasation of blood into the
tissues differing from petechiae only in size. See also
Petechia and Purpura.
- Edema
- an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the cavities and
intercellular spaces of the body.
- Em-, en-, in- (prefix)
- into.
e.g. encyst - to enclose in a cyst or sac.
- Embolus
- a clot, usually part or all of a thrombus,
carried by a larger vessel and forced into a smaller vessel, thus
obstructing blood flow. See also Embolism
and Thromboembolism.
- Embolism
- the sudden blocking of an artery by a clot of material (embolus).
The process of the formation of an embolus.
- -emesis (suffix)
- vomit.
e.g. hematemesis - vomiting blood.
- -emia (suffix)
- blood.
e.g. lipidemia - excess lipid in the blood.
- Endo- (prefix)
- within.
e.g. endocardium - the inner lining of the heart.
e.g. endometrium - the mucous membrane lining of the uterus.
- Enter(o)- (prefix)
- intestine.
e.g. enteritis - inflammation of the intestine.
- Epi- (prefix)
- upon; over.
e.g. epibulbar - situated upon the eyeball.
- Epicardium
- the inner layer of the serous pericardium which is in contact
with the heart.
- Eroded
- having a shallow or superficial ulceration.
- Etiology
- the causative agent in a lesion.
- Ex(o)- (prefix)
- out of; away from; outside of.
e.g. exophytic - projecting out from a surface.
F
- Fibrin
- a filamentous protein formed from the precursor fibrinogen by
the enzyme thrombin.
- Fistula
- an abnormal, tube-like passage from a hollow organ to the
surface, or from one organ to another.
e.g. esophageal fistula - a communication between the esophagus and some portion of the respiratory tract.
- Flocculent
- having downy or flaky shreds.
- Friable
- breaks apart or crumbles easily.
G
- Gastroenteritis
- inflammation of the lining of the stomach and intestine.
- -genesis(suffix)
- origin.
e.g. spermatogenesis - formation of sperm.
- Granuloma
- a focal collection of activated macrophages.
- Granulomatous
- composed of granulomas.
- Grey matter
- the grey nervous tissue of the brain and spinal cord consisting
of the cell bodies and dendrites of nerve cells rather than the
myelinated axons.
- Grumose
- lumpy or clotted.
H
- Hema-, hemato, haemo- (british)- (prefix)
- blood
e.g. hematocrit - the volume percentage of erythrocytes in whole blood.
- Hemangio- (prefix)
- blood vessel.
e.g. hemangiosarcoma - malignant tumor of a blood vessel.
- Hematoma
- a localized collection of extravasated blood, usually clotted.
- Hereditary
- transmitted from parent to offspring; derived from ancestry. See
also Congenital.
- Hetero- (prefix)
- dissimilar.
e.g. heterocellular - composed of more than one type of cell.
- Histiocyte
- a large, phagocytic cell of the reticuloendothelial system; a
macrophage.
- Histiocytoma
- a common neoplasm of young dogs composed of round
histiocytic cells, thought to be
Langerhan's cells. Most tumors spontaneously regress.
- Homeo-, homo- (prefix)
- similar; same.
e.g. homeotypical - resembling the normal or usual type.
- Hydro-, hygro- (prefix)
- water; fluid.
e.g. hydronephrosis - distension of the renal pelvis and calices with urine.
- Hydroureter
- distension of the ureter with fluid due to obstruction.
Hydroureter is often accompanied by hydronephrosis if the
obstruction is in the bladder trigone or more distal.
- Hyper- (prefix)
- above and beyond; excessive.
e.g. hyperacidity - excessive acidity.
e.g. hyperchromasia - excessive pigmentation
- Hyperemia
- presence of an increased amount of blood in a part or an organ.
- Hypertrophy
- an increase in the size of a cell, tissue or organ usually as a
physiologic response to a stimulus.
- Hypoplasia
- underdevelopment of a tissue or organ usually due to a decrease
in the number of cells.
- Hypotonia
- abnormally decreased tonicity, tension or strength; ocular
hypotony refers to low intraocular pressure.
I
- -iasis (suffix)
- a process, especially a morbid one.
e.g. amebiasis - the state of being infected with amebae.
- Idiopathic
- occurring without known cause.
- Imperforate
- atretic; closed.
- Indurated
- abnormally hard.
- Infarct
- a localized area of ischemic necrosis
produced by the occlusion of the blood vessels - either arterial
supply or venous drainage.
- Infra- (prefix)
- beneath.
e.g. infraorbital - beneath the eye.
- Inter- (prefix)
- between.
e.g. intercellular - between two cells.
- Intra- (prefix)
- within.
e.g. intracellular - within cells.
- Ipsilateral
- affecting or pertaining to the same side.
- Ischemia
- a local deficiency of blood due in part to functional
constriction or actual mechanical obstruction of a blood vessel.
- -itis (suffix)
- inflammation.
e.g. appendicitis - inflammation of the appendix.
J
K
L
- Leio- (prefix)
- smooth.
e.g. leiomyoma - a benign tumor of smooth muscle cells.
- Lesion
- an alteration or abnormality in a tissue or cell; a pathological
change.
- Leuc-, leuk- (prefix)
- white.
e.g. leukocyte - a white blood cell.
e.g. leukopenia - reduction in the number of leukocytes in the blood.
- Leukoencephalitis
- inflammation of the white matter of
the brain.
- Lip(o)- (prefix)
- fat; lipid.
e.g. lipoma - a benign tumor of fat cells.
- Lith- (prefix)
- stone.
e.g. lithotomy - removal of a stone.
- Lymphangiectasia
- dilation of the lymphatic vessels; may be congenital or
acquired.
- Lymphoma
- a neoplastic disorder of lymphocytes.
- -lysis (suffix)
- to dissolve.
e.g. autolysis - self-dissolution.
M
- -malacia (suffix)
- softening.
e.g. osteomalacia - softening of the bone.
- Macro- (prefix)
- large.
e.g. macrophage - a large, mononuclear, phagocytic blood cell.
- Malignant
- having the properties of anaplasia, invasiveness and metastasis;
Tending to become progressively worse and to result in death. See
also Cancer.
- Malposition
- faulty or abnormal position of a part of the body. See also
Dystopia.
- Mega- (prefix)
- great.
e.g. megakaryocyte - the giant cell of the bone marrow that has a greatly lobulated nucleus and gives rise to blood platelets.
- -megaly (suffix)
- great, large.
e.g. splenomegaly - enlargement of the spleen.
- Melan- (prefix)
- black.
e.g. melanin - black pigment of the hair, skin, ciliary body, choroid, retina, and certain nerve cells.
- Meninges
- the three membranes covering the brain and spinal cord - the
dura mater, arachnoid, and pia mater.
- Meningo- (prefix)
- membrane; meninges.
e.g. meningoencephalitis - inflammation of the brain and its meninges.
- Mesothelium
- the layer of flat cells lining the body cavity of the embryo; in
the adult, it forms the simple squamous epithelium that covers the
true serous membranes of the body. Mesothelium
is derived from mesoderm.
- Metastatic
- a tumor that has transfered from one organ (or part) to another
not directly connected to it. See also Cancer.
- Micro- (prefix)
- small.
e.g. microhepatia - a small liver.
- Morphologic diagnosis
- the interpretation of the abnormalities in terms of severity,
time, lesion and anatomic site. For example: severe, chronic,
glomerulonephritis.
- Mucous
- (adj.) relating to or resembling mucus.
- Mucus
- (n.) the glandular, free slime of the mucous membranes.
- My-, myo- (prefix)
- muscle.
e.g. leiomyosarcoma - a malignant tumor of smooth muscle cells.
- Myelin
- the lipid substance forming a sheath around the axons of certain
nerve fibers.
- Myx- (prefix)
- mucus.
e.g. myxedema - mucinous edema (swelling).
N
- Necr- (prefix)
- death.
e.g. necrosis - the morphologic changes indicative of cell death, indicated by characteristic nuclear and cytoplasmic changes.
- Necropsy
- examination of a body after death.
- Nephr- (prefix)
- kidney.
e.g. nephrectomy - surgical removal of the kidney.
O
- -oid (suffix)
- like, resembling.
e.g. leukemoid - like leukemia.
- Oligo- (prefix)
- few; scanty.
e.g. oligochromemia - deficiency of hemoglobin in the blood.
- -ologous (suffix)
- relating to.
e.g. homologous - of similar structure.
- -oma (suffix)
- tumor.
e.g. osteoma - tumor of bone.
- -opathy (suffix)
- disease.
e.g. nephropathy - any disease of the kidney.
- -orrhea (suffix)
- flow; discharge.
e.g. leukorrhea - white discharge.
- -oscopy (suffix)
- view.
e.g. endoscopy - to view the inside, specifically: the intestine.
- -osis (suffix)
- a process, especially a morbid one.
e.g. diverticulosis - involvement with diverticula.
- Osteo- (prefix)
- bone.
e.g. osteomyelitis - inflammation of bone.
- Osteoid
- resembling bone.
- -ostomy (suffix)
- mouth.
e.g. gastrostomy - creation of an artificial gastric fistula.
- -otomy (suffix)
- cut.
e.g. cholecystotomy - incision into the gallbladder.
P
- Panniculitits
- a rare, multifactorial inflammatory condition involving
subcutaneous fat.
- Panniculus
- a layer of membrane.
- Papillary
- having small nipple-shaped projections.
- Papilloma
- the common wart; a benign tumor derived from epithelium. They
are caused by papillomaviruses.
- Papules
- a small circumscribed, solid, elevated lesion of the skin.
- Para- (prefix)
- beside.
e.g. para-aortic - beside the aorta.
e.g. parauterine - beside the uterus.
- Parenchyma
- the essential or functional elements of an organ.
- Patent
- open, exposed or unobstructed.
e.g. patent ductus arteriosus - an abnormal persistence after birth of an open lumen in the ductus arteriosus, between the pulmonary artery and the aorta.
- Pathogenesis
- the sequence of events that leads to a disease or morbid
process. It may be, for example, hormonal, chemical, infectious,
genetic or traumatic in nature.
- Pathology
- the science and study of disease, especially the causes and
development of abnormal conditions both gross and microscopic.
- Pedunculated
- elevated, as on a stem (peduncle).
- -penia (suffix)
- poverty.
e.g. thrombocytopenia - decrease in blood platelets.
- Peri- (prefix)
- around.
e.g. peribronchial - around the bronchus.
- Pericardium
- the fibroserous sac enclosing the heart and the roots of the
great vessels of the heart. It is composed of a fibrous external
layer and a serous inner layer.
- Petechia
- a pinpoint, non-raised, purplish-red spot caused by intradermal
or subcutaneous hemorrhage. Plural is petechiae. These are tell-tale
symptoms of Ebola and Lassa Fevers.
- Peyer's Patches
- ovoid, elevated patches of closely packed lymphoid follicles in
the mucosa and submucosa of the small intestine. Also called
aggregated lymphoid follicles.
- -phage (suffix)
- eat; devour.
e.g. macrophage - a cell which devours (phagocytoses).
- Phago- (prefix)
- eat; devour.
e.g. phagocyte - any cell that ingests foreign material, other cells or microorganisms.
- Pheochromocytoma
- (pheo=dusky) (chromo=color) (cyt=cell) (oma=tumor)
a small tumor of chromaffin cells, usually of the adrenal medulla, but occasionally of the chromaffin tissue of sympathetic paraganglia. Functional tumors secrete catecholamines.
- Phleb- (prefix)
- vein.
e.g. phlebitis - inflammation of the vein.
- Pinna
- the projecting part of the ear; also known as the auricle.
- -plasia (suffix)
- to form.
e.g. hyperplasia - an increase in the number of cells in a tissue or organ, usually as a physiologic response to a stimulus.
- -pnea (suffix)
- breath.
e.g. dyspnea - labored or difficult breathing.
- Polyp
- a spheroidal mass that protrudes upwards or outwards from a
normal surface. Polyps may be hyperplastic,
inflammatory, or neoplastic.
e.g. pedunculated polyp - a polyp attached by a thin stalk (peduncle).
e.g. sessile polyp - a polyp with a broad base (sessile).
- Polypoid
- Resembling a polyp.
- Purpura
- a hemorraghic disease characterized by extravasation of blood
into the tissues producing spontaneous
ecchymoses and petechiae.
- Pus
- a protein-rich liquid inflammation product comprised of
leukocytes, a thin fluid and cellular
debris.
- Prognosis
- a prediction of the outcome of the pathological process or
disease.
- -ptosis (suffix)
- falling.
e.g. ptosis - drooping, specifically: of the eyelid.
- Pyo- (prefix)
- pus.
e.g. pyometra - an accumulation of pus within the uterus.
e.g. pyogranuloma - an infiltration of polymorphonuclear cells into an area of chronic inflammation characterized by mononuclear cells, macrophages, lymphocytes and even plasma cells.
- Pyelonephritis (nephropyelitis)
- inflammation of the kidney and renal pelvis often by ascending
bacterial infection.
Q
R
- Reniform
- shaped like a kidney.
- Resilient
- having the ability to return to an original shape after having
been compressed or deformed.
- -rhage, -rrhage, -rrhagia (suffix)
- discharge.
e.g. hemorrhage - discharge of blood.
- -rrhea (suffix)
- abnormal or excessive flow.
e.g. steatorrhea - excessive lipid in the feces.
S
- Saponification
- the hydrolysis of a fat by alkali with the formation of a soap
and glycerol.
- Sclero- (prefix)
- hard.
e.g. scleroma - a hardened patch of skin or mucous membrane.
- Serosa
- any serous membrane.
- Serous Membrane
- the membrane lining the walls of the body cavities and enclosing
the contained organs. It is a mesothelium
lying upon a connective tissue layer and secretes a watery serous
fluid.
- Serpiginous
- having a wavy border.
- Serrated
- having a saw-like edge.
- Sessile
- attached by a broad base.
- -stasis (suffix)
- standing still.
e.g. hemostasis - arrest of blood circulation.
- Stea- (prefix)
- lipid.
e.g. steatorrhea - excessive lipid in the feces.
- Stenosis
- a stricture of any canal.
- Stoma- (prefix)
- mouth.
e.g. stomatology - the study of the mouth and its diseases.
- Stomatitis
- inflammation of the mucosa of the mouth.
- Suppurative
- containing pus.
- Syncope
- a temporary loss of consciousness due to insufficient cerebral
blood flow; fainting.
T
- Thromboembolism
- the lesion created by a thromboembolus.
- Thromboembolus
- a clot of material that breaks free from a primary site, is
transported in the bloodstream and becomes lodged and adhered at a
secondary site.
- -trophy (suffix)
- nourish.
e.g. dystrophy - defective or faulty nutrition.
U
- Ulcerated
- having a local defect or excavation of the epithelium of an
organ or tissue through the basement membrane.
- Umbilicated
- marked by depressed spots resembling the umbilicus.
- Umbilicus
- the scar marking the site of entry of the umbilical cord into
the fetus.
- Unilateral
- affecting only one side.
- -uria (suffix)
- urine.
e.g. proteinuria - protein in the urine.
V
- Verruca
- a wart.
- Verrucous
- rough; wart-like.
- Viscous
- thick, coagulated; sticky or gummy.
W
- White matter
- the white nervous tissue of the brain and spinal cord consisting
of the conducting, myelinated fibers.
X
- Xantho- (prefix)
- yellow.
e.g. xanthoma - a yellow tumor.
Y
Z